Last Updated on 2025-05-19
In the current era of information technology, software security is an absolute must. It is crucial to be aware of the major software security threats that could potentially ruin your project.
We delve into the risks associated with software safety and provide effective strategies to combat these threats.
Understanding the Digital Battlefield
Software security is crucial in today’s digital world. It involves creating secure software systems that can resist attacks and vulnerabilities. Identifying threats early, using secure architecture design, following best coding practices, and rigorous testing are essential.
By implementing software security measures, organizations can protect their assets and customers. Insecure software can cause cyberattacks, data breaches, and disruptions, making software security necessary.
The State of Cybersecurity in IT
The current state of cybersecurity is a complex and evolving topic that requires a comprehensive approach to protect against cyber threats. According to a report by ISACA, cybersecurity practices and measures are slowly getting better.
On the other hand, the scale of the cybersecurity challenge has grown dramatically, with the number of cybercriminals skyrocketing, their organizational ability growing, and the potential damage from a cyberattack being catastrophic.
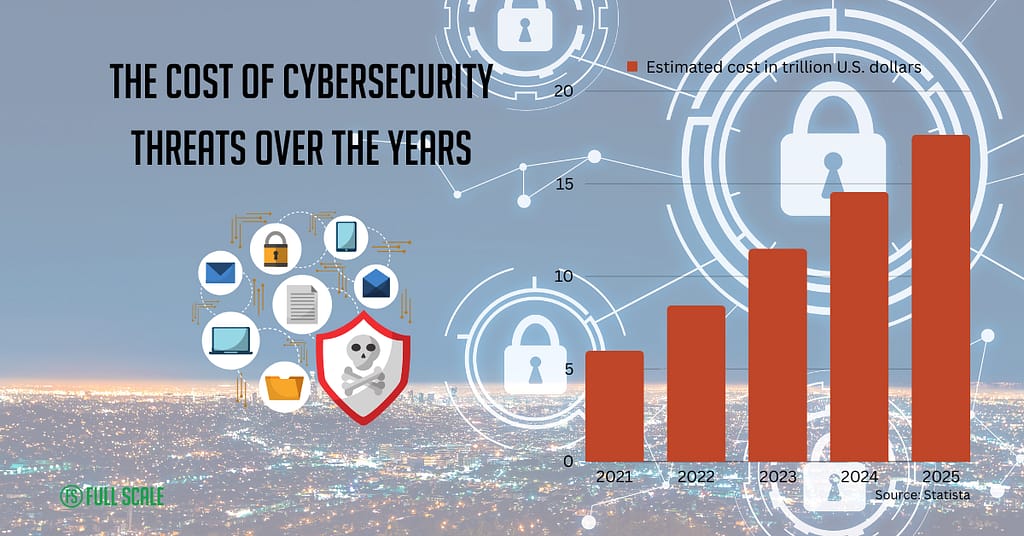
That’s why cybersecurity is a critical topic in the IT industry. Organizations must align their cybersecurity programs to business objectives, invest in cybersecurity, and stay up-to-date with the latest cybersecurity trends and software security threats.
Key Challenges in Protecting Digital Assets
In the era of relentless cyber threats, safeguarding digital assets poses significant challenges:
- The sophistication of attacks is ever-increasing, with adversaries utilizing state-of-the-art technologies to bypass conventional defenses.
- The sheer volume of attacks can be overwhelming, making prioritizing and responding effectively tricky. Add to this the expansive and evolving landscape of IT, with cloud services and the Internet of Things (IoT) widening the potential attack surface.
- There’s a persistent talent gap in cybersecurity, leaving many organizations needing more in-house expertise to fortify their defenses adequately.
Protecting digital assets is a complex and evolving topic that requires a comprehensive approach to protect against cyber threats. Organizations must align their cybersecurity programs to business objectives, invest in cybersecurity, and stay up-to-date with cybersecurity trends and threats.
The Spectrum of Software Security Threats
The spectrum of security software threats is broad and encompasses a wide range of malicious activities and vulnerabilities that can impact the security of software systems. Understanding this spectrum is crucial for developing effective security measures.
Malware Attacks Unpacked
Malware, short for malicious software, is harmful software designed to compromise computer systems, networks, or users. It aims to disrupt normal computing operations and compromise data confidentiality, integrity, or availability.
There are various malware attacks, each with specific characteristics and purposes. Some common types of malware include:
- Viruses attach themselves to clean files and spread uncontrollably, corrupting system functionality and compromising data.
- Worms exploit network vulnerabilities without human intervention to spread and often deliver harmful payloads.
- Trojans disguise as legitimate software, tricking users into executing them to create backdoors for further exploitation.
- Ransomware locks and encrypts your data, demanding payment for its release – without any promises.
- Cryptojacking silently uses your system’s resources for mining cryptocurrency, affecting performance and energy costs.
- Spyware infiltrates systems to steal sensitive information, often without the user’s knowledge.
- Adware tracks online behavior to bombard users with unwanted advertisements, potentially breaching privacy.
Awareness of various types of malware, including the dangerous ransomware attack, helps better prepare and protect against potential cyberattacks.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) Exposed
An Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) takes cyberattacks to a more menacing level. APTs are highly sophisticated, often state-sponsored or financially motivated actors targeting high-value organizations or nations.
Unlike smash-and-grab cybercrime, APTs play a long game, infiltrating quietly and maintaining a foothold for months or even years. They’re after sensitive information, intellectual property, or national security data, stealthily monitoring and escalating their access over time.
Indicators hinting at an APT include uncharacteristic outbound data traffic, strange user account activities, backdoor malware to maintain access, and unexpected database operations with large data volumes.
Mitigating the risks associated with APTs requires a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that includes:
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly monitor network traffic, system logs, and behavior analytics to detect unusual or suspicious activities.
- Threat Intelligence: Stay updated using threat intelligence feeds on the latest attack methods and security weaknesses.
- Team member Training: Train employees to recognize and avoid social engineering attacks, especially spear-phishing.
- Network Segmentation: To prevent hackers from moving around undetected, divide the network into smaller sections called network segmentation.
- Endpoint Protection: Use advanced endpoint protection solutions to detect and prevent APT-related malware.
Given the evolving nature of APTs, organizations should prioritize a proactive and adaptive security posture, regularly assess their defenses, and collaborate with the broader cybersecurity community to share threat intelligence.
Defensive Strategies Against Common Threats
Protecting against software threats is a critical concern for businesses in today’s digital world. Common cybersecurity threats include malware, social engineering, software supply chain, APT, distributed denial of service (DDoS), man-in-the-middle attacks (MitM), password attacks, and emerging information security threats.
To defend against these threats, organizations must take a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity. Here are some defensive strategies that can help protect against common software threats:
- Implement a multi-layered security approach: The security measures include firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and more.
- Keep software up-to-date: Regularly patching software vulnerabilities can help prevent cyberattacks.
- Use strong passwords: Strong passwords can help prevent password attacks.
- Train employees on cybersecurity best practices: Educate team members to prevent social engineering attacks through cybersecurity best practices.
- Encrypt sensitive data: Encryption can help protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Protecting against software threats requires a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity. Organizations must prioritize the protection of critical information assets by investing in cybersecurity and staying up-to-date with the latest cybersecurity trends and threats.
Combating Viruses and Worms
Combating viruses and worms requires a multi-layered approach that combines technical measures, user education, and proactive security practices. Here are five effective ways to combat viruses and worms:
- Install and Update Antivirus: To keep your systems safe, install reputable antivirus and anti-malware software on all your devices. Ensure the software is regularly updated with the latest virus definitions to detect and remove known threats.
- Keep Systems and Software Updated: Update security software frequently to protect devices against threats. Do the same with the OS and minimize redundant system storage. This helps close known vulnerabilities and reduces the risk of exploitation by viruses and worms.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Train members regularly on security awareness to educate them about malware risks, including viruses and worms. Train members to recognize and avoid phishing emails, suspicious links, and untrusted downloads to prevent security breaches and protect the organization from cyber threats.
- Use Firewalls and Network Security Measures: Install firewalls to control network traffic and enhance security. Configure firewalls to block unauthorized access and prevent the spread of worms within the network. Use intrusion detection systems and monitor your network and computer systems to stop harmful activity quickly. Take immediate action upon detecting any suspicious behavior.
- Backup Critical Data and Implement Recovery Plans:
Regularly back up critical data and store backup copies in a secure and isolated location. This ensures that critical information can be recovered in case of a virus or worm attack. Develop and regularly test an incident response and recovery plan. This plan should outline the steps to take in the event of a malware infection, including containment, eradication, and data restoration.
Bonus Tip: Implement Least Privilege Access:
Grant users only the necessary level of access required for their job functions by following the principle of least privilege. This limits the impact of malware by restricting unauthorized actions.
Combating viruses and worms involves preventive measures, user education, and responding effectively to security incidents. Organizations should stay informed about emerging threats, continuously assess their security posture, and adapt their strategies to evolving cyber threats.
Neutralizing Botnets and DDoS Assaults
Neutralizing botnets and mitigating Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks can be challenging, but several strategies can help enhance your defenses. Here are some of the most effective ways to neutralize botnets and DDoS assaults:
- Implement DDoS Protection Services:
Utilize specialized DDoS protection services offered by reputable cybersecurity providers. These services often involve deploying hardware and software solutions to filter out malicious traffic before it reaches your network.
- Configure Firewalls and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS):
Configure firewalls and IPS devices to identify and block suspicious traffic. Keep these devices updated with the latest threat intelligence to recognize and block traffic patterns associated with botnets and DDoS attacks.
- Traffic Analysis and Anomaly Detection:
Implement network traffic analysis tools and anomaly detection systems to monitor and identify unusual traffic patterns. Unusual spikes in traffic or deviations from normal behavior may indicate a DDoS attack. Automated systems can then trigger responses or alerts to mitigate the impact.
- Rate Limiting and Traffic Shaping:
Use rate limiting and traffic shaping mechanisms to control incoming traffic flow. This can help prevent sudden spikes that are characteristic of DDoS attacks. By regulating the rate at which traffic is allowed into your network, you can reduce the impact of volumetric attacks.
- IP Blocklisting and Safelisting:
Maintain a blocklist of IP addresses associated with botnets and DDoS attacks and regularly update it to block traffic from these sources. Conversely, use safelists only to allow traffic from trusted sources. However, remember that IP blocklisting may not be foolproof, as attackers can frequently change IP addresses.
Remember, a comprehensive security strategy combines these techniques and continuous monitoring and adaptation to emerging software security threats. Regularly update your security measures, train personnel on cybersecurity best practices, and consider consulting with cybersecurity experts to stay ahead of evolving threats.
Targeted Attack Prevention Techniques

It is important to understand that no one solution can ensure complete protection against targeted attacks. A holistic and adaptive security strategy, combined with regular risk assessments, is essential for staying ahead of evolving software security threats.
How to Shield Against Phishing and Social Engineering
Protecting against phishing and social engineering requires a combination of technical defenses, user education, and proactive security measures. Here are effective ways to shield against these threats:
- Training and Awareness: Regular security awareness training is crucial to help employees recognize and prevent phishing and social engineering attacks. Provide practical examples and scenarios to make the training relevant.
- Email Filtering and Authentication: Use advanced email filtering to detect and block phishing emails before they reach users’ inboxes. Using email authentication protocols such as DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), SPF (Sender Policy Framework), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) can aid in verifying the legitimacy of incoming emails.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Use MFA to secure critical systems and accounts. MFA offers an additional layer of security, requiring extra verification in case of a phishing incident.
- Regular Security Audits and Simulations: Conduct regular security audits and simulated phishing exercises to assess the organization’s vulnerability to social engineering attacks. These simulations help identify weak points in the security posture and allow for targeted training and awareness programs.
- Strict Access Controls and Least Privilege Principle: Limiting access to data and systems based on job requirements can reduce the impact of social engineering attacks.
- Verify Requests for Sensitive Information: Authenticate requests for sensitive information or financial transactions using a separate communication channel before sharing the data.
Stay safe from phishing and social engineering attacks, use multiple strategies, update your security protocols, and stay informed about new threats. Remember that software security is constantly changing, so it’s essential to remain vigilant.
Steps to Block Drive-By Downloads and Exploit Kits
Drive-by downloads and exploit kits are common methods used by cybercriminals to infect devices with malware. To protect systems, follow these steps:
- Keep Software and Systems Updated: Regularly update and patch all software, including operating systems, web browsers, plugins, and other applications. Drive-by downloads often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software. Enable automatic updates where possible to ensure timely patching.
- Use Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): Use a WAF to protect your web application by monitoring and filtering HTTP traffic from the Internet. This will help detect and block malicious requests, preventing attacks that exploit vulnerabilities in your web application.
- Browser Security Settings: Secure web browsers by turning off unnecessary plugins, scripts, and active content. Set up prompts for file downloads and block potentially harmful content. Educate users on safe browsing practices.
- Network Security Measures: Use IDPS to secure your network by analyzing traffic for exploit kit activity patterns and blocking potential threats.
- Endpoint Protection and Anti-Malware Software: Install strong endpoint protection and anti-malware software on all devices. Update the security software regularly to improve the detection of malicious files and activities.
- User Education and Awareness: Educate users about the risks associated with drive-by downloads and exploit kits. Be cautious when visiting unfamiliar websites, be skeptical of unexpected download prompts, and avoid clicking on suspicious links. Regularly train users to recognize social engineering tactics.
A multi-layered security strategy is crucial as only some solutions can provide complete protection. Use technical measures, user education, regular audits, and monitoring for unusual activity. Implement a comprehensive incident response plan to respond quickly and effectively to security incidents.
Securing the Software Frontline
Securing the software frontline requires a holistic and proactive approach that spans the entire software development lifecycle. By integrating security into the development process, fostering a security-aware culture, and leveraging automation, organizations can better protect their software assets from evolving cyber threats.
Patch Management and Vulnerability Mitigation
Effective patch management and vulnerability mitigation are crucial for maintaining a secure IT environment. Here’s how you can ensure your defenses remain robust:
| Patch Management and Vulnerability Mitigation Best Practices | |
| Patch Management | Vulnerability Mitigation |
| Automate the Patching Process: Embrace automated patch management systems to ensure patches are applied as soon as they’re available without delays. | Conduct Risk Assessments: Regularly assess your IT infrastructure to identify and evaluate vulnerabilities. |
| Prioritize Based on Risk: Assess vulnerabilities and prioritize patching based on potential impact, starting with the most critical ones. | Embrace Endpoint Protection: Implement endpoint protection tools to identify and automatically respond to threats. |
| Test Before Deployment: Verify patches in a controlled environment before a full rollout to prevent complications in your live systems. | Enforce Least Privilege: Limit user access rights strictly to what’s necessary for their role, reducing the attack surface for potential exploitation. |
| Consistent Monitoring: Continuously monitor for new vulnerabilities and ensure your patch management solution is up-to-date with new threats. | Implement Network Segmentation: Keep sensitive data and critical systems isolated to minimize the fallout if a breach does occur. |
| Audit Regularly: Conduct regular audits to ensure all systems are compliant with your patching policies and no device is left unpatched. | |
Maintaining a rigorous patch management and vulnerability mitigation strategy lessens the likelihood of security breaches and the ensuing damage they might cause.
Implementing Robust Access Controls and Encryption
Implementing robust access controls and encryption is vital in securing your IT systems. Here’s how to enhance your defensive posture:
| Access Control and Data Encryption Measures | |
| Access Control | Data Encryption |
| Employ Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on the individual’s role within your organization, ensuring they only have access to the information necessary for their duties. | Encrypt Sensitive Data: Secure sensitive in-transit and at-rest data with strong encryption to prevent unauthorized access. |
| Utilize Strong Authentication Mechanisms: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for an added layer of security, requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to access sensitive systems. | Key Management: Employ robust key management strategies to ensure encryption keys are securely stored and managed, preventing unauthorized access to encrypted data. |
| Regularly Review Access Rights: Make it a routine to review user privileges and adjust or revoke them as necessary, especially after role changes or terminations. | Use Trusted Encryption Tools: Choose reputable, regularly updated encryption tools that comply with industry standards. |
Implementing access controls and encryption can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized data access. In case of a data breach, sensitive information remains unreadable and secure.
Future-Proofing IT with Smart Security Innovations
Future-proofing IT with smart software security innovations involves adopting strategies and technologies that address current security challenges and anticipate and adapt to emerging threats.
Embracing Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning
Embracing predictive analytics and machine learning is a forward-thinking approach to IT security, providing the ability to identify and respond to threats preemptively.
Benefits of Predictive Analytics:
- Anticipate Future Security Incidents: By analyzing trends and patterns, predictive analytics can forecast potential security breaches before they occur.
- Enhanced Threat Intelligence: Machine learning algorithms constantly evolve, learning more effectively from new data to recognize threat signatures and anomalous behavior.
- Faster Incident Response: Predictive models can trigger automated responses to suspected threats, reducing response times dramatically.
Applying Machine Learning:
- Automated Anomaly Detection: Machine learning excels at identifying deviations from normal behaviors, which could indicate a security incident.
- Adaptive Security Posture: Your security systems can adapt over time, adjusting to the evolving threat landscape without manual reprogramming.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: IT teams can improve efficiency by using predictive insights to prioritize high-risk areas.
Integrating machine learning and predictive analytics into your IT security strategy can help create a more competent defense against emerging threats.
Integrating Behavioral Analysis for Real-Time Protection
Integrating behavioral analysis into your software security protocol provides a dynamic layer of real-time protection. Unlike traditional security measures, behavioral analysis focuses on how users and systems typically behave, making it easier to spot anomalies that may indicate a breach.
Implementing User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA):
- Baseline Normal Activity: First, establish what ‘normal’ looks like in your environment to detect anomalies. UEBA systems use machine learning to understand typical user behaviors and entity activity patterns.
- Identifying Risky Behavior: UEBA solutions assign risk scores based on deviations from established norms. These scores help security teams prioritize the most serious threats.
- Timeline Analysis for Threat Detection: By stitching together related events into a coherent timeline, analysts can better assess the scope of a potential threat.
Behavioral analysis is particularly adept at identifying insider threats and compromised user credentials. By monitoring for unusual access patterns or atypical data transfers, behavioral analysis helps to counter threats that traditional security measures might miss.
Advantages of Real-time Behavioral Analysis:
- Quick Detection: Identify threats as they occur, not after the damage is done.
- Reduced False Positives: More accurate differentiation between malicious activity and benign anomalies.
- Adaptive: Continuously learns and adapts to the evolving behaviors within your IT environment.
Integrating real-time behavioral analysis into your security framework means staying one step ahead of the attackers by catching them in the act.
Integrating behavioral analysis into your security strategy requires combining technology, data analysis, and human expertise. By continuously monitoring and adapting to evolving threats, organizations can enhance their ability to detect and respond to security incidents in real time.
Practical Tips for a Strong IT Security Posture
Maintaining a strong IT security posture is crucial for safeguarding an organization’s assets and data. Organizations can establish a robust and resilient IT security posture by adopting specific software security steps, better protecting against a wide range of cyber threats. Remember that security is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement and adaptation to the evolving threat landscape.
Team Member Education and Awareness Training
Member education and awareness training are essential elements of a strong IT security posture. By equipping your team with the right knowledge, they become your first line of defense against cyber threats.
Components of Effective Training Programs:
- Identifying Phishing Scams: Teach all members how to recognize signs of phishing and the importance of reporting suspicious emails.
- Password Best Practices: Encourage the use of strong passwords and the adoption of multi-factor authentication.
- Handling Sensitive Data: Instruct on secure ways to manage and share sensitive information.
- Safe Internet Habits: Emphasize the importance of updating software, avoiding suspicious downloads, and utilizing secure connections.
- Incident Reporting Protocols: Ensure that employees understand how and when to report security incidents.
Benefits of Regular Cybersecurity Training:
- Risk Reduction: Educated team members are less likely to fall victim to cyber threats.
- Empowered Workforce: Knowledgeable members can make informed decisions that protect company data.
- Compliance: Training helps meet legal and regulatory requirements related to data protection and privacy.
Remember, the goal is to create an informed culture where cybersecurity is a shared responsibility.
Build Secure Software Today
If you’re looking for a reliable offshore software development partner, Full Scale is for you.
We are a US-based company in the heart of the Midwest with offshore operations in the Philippines.
Our continually growing client base is a testament to the excellent software solutions we provide. We have provided over 1.5 MILLION HOURS of service hours to our global clients.
At Full Scale, we have a pool of dependable software talent, from developers to testers and leaders, who have undergone a stringent hiring process. Our developers will work seamlessly with your development team to help you safely and securely build your MVP from various software security threats.
Hire Your Software Development Team
FAQ: Fortifying Your IT Security
Fortifying IT security involves implementing a comprehensive strategy to protect your organization’s digital assets from cyber threats.
By systematically implementing these measures, organizations can fortify their IT security and create a resilient defense against cyber threats. Keep security measures updated to match the changing threats and the organization’s risk profile.
What Are the First Steps in Establishing an IT Defense Strategy?
When establishing an IT defense strategy, your first steps should be:
- Assess: Perform a risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities within your IT environment.
- Plan: Develop a security plan that includes policies, procedures, and an incident response strategy.
- Educate: Train employees on security best practices and their role in maintaining cybersecurity.
This foundation sets the stage for a robust security posture to protect your digital assets effectively.
How Can Organizations Stay Ahead of Emerging Security Threats?
To stay ahead of emerging security threats, organizations should:
- Invest in Continuous Learning: Stay updated on the latest threat landscape and security technologies.
- Implement Proactive Monitoring: Utilize threat intelligence and predictive analytics to detect potential risks early.
Keeping a finger on the pulse of cybersecurity developments can help preemptively address threats.

Matt Watson is a serial tech entrepreneur who has started four companies and had a nine-figure exit. He was the founder and CTO of VinSolutions, the #1 CRM software used in today’s automotive industry. He has over twenty years of experience working as a tech CTO and building cutting-edge SaaS solutions.
As the CEO of Full Scale, he has helped over 100 tech companies build their software services and development teams. Full Scale specializes in helping tech companies grow by augmenting their in-house teams with software development talent from the Philippines.
Matt hosts Startup Hustle, a top podcast about entrepreneurship with over 6 million downloads. He has a wealth of knowledge about startups and business from his personal experience and from interviewing hundreds of other entrepreneurs.





