Last Updated on 2025-02-27
Our business needs to drive our decisions and our course of action. Where there are problems, there are also solutions.
We’ll focus on two business solutions disrupting the IT industry: offshore vs. outsourcing. Both offshore and outsourcing share their unique advantages. You must also know which venture to sail to meet your demands. But what are their differences? Let’s find out.
Outsourcing and offshoring are two terms that are synonymous with each other. As prevalent as the two are in many service and business processing industries, offshoring is still often confused with outsourcing and vice versa.
At some point in a company’s growth, requiring additional workforce to supplement the business process operations becomes essential to move forward. So, not only do the two pose a conflict in definition but also in each business decision.
Defining the Terms: Offshoring vs Outsourcing
Outsourcing and offshoring are related but are distinct business practices.
What is outsourcing?
Outsourcing is a strategic business practice involving contracting specific tasks or functions to external service providers. Instead of doing everything in-house, companies employ this approach to tap into the expertise of specialized vendors for certain roles.
Typically, firms outsource non-critical activities, allowing them to focus on core tasks and attain maximum internal efficiency. Examples of often outsourced business operations include IT management, accounting, customer service, and marketing.
What is offshoring?
On the other hand, offshoring involves relocating a company’s certain operations to another country. It is often done to capitalize on various benefits specific to the offshore country, such as lower labor costs, favorable regulations, or access to specialized skills and services.
Offshoring can involve either an in-house team in a different geographical location or an outsourced team from a local company in the offshored site. This practice of offshoring can help businesses save on labor costs and resources, operate 24/7 across different time zones, and facilitate access to a broader market or specialized expertise.
Benefits of Outsourcing
Outsourcing can offer various benefits to organizations. Here are some of its commonly cited advantages:
- Cost Efficiency on Lower Labor Cost and Infrastructure Savings: Lower labor costs can significantly reduce operational expenses, particularly for tasks that don’t require on-site presence or specific local expertise. Companies can avoid hefty investments in infrastructure, equipment, and technology by leveraging the existing resources of outsourcing partners.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Outsourcing allows companies to concentrate on their core business activities and strategic objectives. Non-core functions, such as IT support, customer service, or data entry, can be delegated to external experts, freeing internal resources for more critical tasks.
- Access to Specialized Skills and Expertise: It provides you access to a global talent pool, enabling organizations to tap into specialized skills and expertise that may only be available in some places. This is particularly advantageous for tasks requiring specific knowledge or technical capabilities.
- Flexibility and Scalability: It also offers flexibility in adapting to changes in workload or business demands. Your organization can quickly scale your operations up or down based on project requirements without the challenges associated with managing an in-house workforce.
- Time Savings and Faster Time-to-Market: It accelerates project timelines by allowing tasks to be completed more efficiently. External service providers, often specialists in their field, can leverage their experience and resources to deliver results faster, helping organizations meet tight deadlines and get products or services to market more quickly.
While these benefits can be significant, successful outsourcing requires careful consideration of vendor selection, communication strategies, and ongoing management to ensure a positive and productive partnership.
Specialized Outsourcing Services
Outsourcing firms often offer specialized services, providing better efficiency than companies might achieve in-house. There are numerous outsourcing sub-industries, and some of them include:
- Manufacturing Outsourcing: Businesses hire external companies to manufacture their products. This allows them to leverage the expertise of these firms and focus on other essential tasks.
- Business Process Outsourcing (BPO): This involves hiring specialized companies to handle back-office tasks such as customer service and data processing.
- IT Outsourcing: Here, a company’s IT infrastructure is hosted and managed by a third-party provider. This helps keep up with rapid technological changes and frees up internal resources.
- Software Development Outsourcing: Companies contract other companies, like Full Scale, to build software products, significantly reducing development time and cost.
- Project Outsourcing: When specialized help is needed to complete a complex project, companies turn to outsourcing.
- Design Outsourcing: Outsourcing design tasks to companies can help obtain professional custom designs ranging from logos to websites to products.
Companies choose specialized outsourcing services based on their unique needs. They seek providers with expertise in specific areas to enhance overall operational performance.
Offshoring: Moving Forward
Offshoring has a slight edge against outsourcing due to the guaranteed increase in profit in the long run. The basis of this is the retention and acquisition of new clients and the huge cost savings from lower production and labor costs in offshoring countries.
New Models of Offshoring
The offshoring landscape continues to evolve, and new models have emerged in response to changing business dynamics, technological advancements, and global economic trends.
Here are some new models of offshoring that have gained prominence in recent years:
- Global Business Services (GBS)—Involves consolidating various business support functions, such as finance, human resources, IT, and procurement, into a centralized shared service center. This center may be in a different country, often chosen for its cost advantages.
- Nearshoring—It’s a model where companies choose to relocate their business processes to a nearby or neighboring country rather than one far away. This is often done to maintain cultural and geographical proximity while benefiting from cost advantages.
- Cloud Sourcing—Involves remotely accessing business services and resources through cloud-based platforms. This can include outsourcing various functions to cloud service providers, often located in different geographic regions.
- Crowdsourcing—This entails outsourcing tasks or projects to a large, often global, network of individuals or freelancers. Companies can tap into the skills and expertise of a diverse crowd to complete specific assignments.
- Smartshoring—Refers to the strategic allocation of tasks or functions to locations based on each location’s specific strengths and capabilities. It involves a more nuanced approach to offshoring, considering factors beyond cost, such as skill sets and innovation capabilities.
- Agile Offshoring—Involves applying agile methodologies to offshoring processes, emphasizing collaboration, flexibility, and iterative development. It is particularly relevant in software development and IT projects.
These new offshoring models reflect the evolving nature of global business practices. These models emphasize efficiency, collaboration, and flexibility in response to the demands of a rapidly changing business environment.
Offshoring Economics
The economics of offshoring involve a complex interplay of various factors that impact the costs, benefits, and overall economic implications for businesses and countries involved. As controversial as it sounds, the offshoring system bolsters developing countries’ economies and further promotes the concept of globalization.
Understanding the benefits and risks of offshoring requires a comprehensive analysis of different factors, specific circumstances, and the companies’ goals.
Benefits and Risks of Offshoring to Businesses
The following are some notable benefits and risks that offshoring can bring businesses:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Lower Labor Costs: By relocating to countries with lower wage rates, companies can significantly reduce labor costs, enabling them to reinvest savings into other business areas. | Communication Challenges: Time zone differences and language barriers can complicate effective communication, potentially slowing project completion. |
| Increased Productivity: Offshore teams often demonstrate high productivity levels. Whether they’re answering customer queries or handling paperwork, every increase in efficiency bolsters overall profits. | Project Control: Maintaining control over project quality and outcomes from a distance can be challenging due to a lack of immediate oversight. |
| Business-Friendly Regulations: Countries like the Philippines often present fewer regulatory hurdles, making the offshoring process easy and quick. Faster paperwork processing and minimal regulatory issues are advantages for businesses seeking to establish offshore operations. | Political and Economic Instability: Changes in the political or economic climate in offshore locations may disrupt operations and impact the ability to do business. |
| Expanded Customer Base: Offshoring can enable access to customers in the host country and other nations, boosting international market presence. | Reputation Risks: Companies that offshore can face reputational risks related to the perception of shipping local jobs overseas. |
| Insight into Market Trends and Risks: Establishing a business in an offshore location can help companies better understand those markets, enabling them to manage risks and opportunities more effectively. |
While offshoring offers these benefits, it’s important for organizations to carefully consider the potential challenges, such as cultural differences, communication barriers, and the need for effective management strategies.
It’s important to evaluate these benefits and risks carefully while formulating an offshoring strategy. Successful offshoring requires thorough planning, clear communication, and strong partnerships with offshore service providers.
Benefits to Offshore Nations
Offshoring also presents numerous benefits for the host nations, including:
- Economic Growth: Offshoring injects foreign income into the host nations’ economy, leading to economic development. India’s offshoring industry, for instance, has elevated its status to the world’s third-largest economy.
- Job Creation: Offshoring creates employment opportunities in the host nation. For instance, the BPO industry in the Philippines supports 1.3 million jobs.
- Infrastructure Development: The demands of offshoring companies often push the host nations to improve their infrastructure, particularly in the technology and transport sectors.
- Improved Standard of Living: By stimulating economic growth and providing job opportunities, offshoring can contribute to an improved standard of living in the host nations.
- Knowledge and Skills Transfer: Offshoring companies often train their employees in the host nations, transferring knowledge and skills.
Mitigate Uncertainty with a Managed Offshore Outsourcing Model
One way to mitigate the control drawbacks associated with offshoring is through a managed offshore outsourcing model. This strategy brings the best of offshoring and outsourcing, empowering companies with control over their operations while decreasing the risk of potential disruptions. Here’s why:
- Reduced Risk: In this model, the risks tied to political or social disruptions rest with the service provider, not the contracting company.
- Optimal Control: With offshore workers integrated into the team, businesses have more control over their operations compared to traditional outsourcing models.
- Flexibility: Companies can scale their offshore teams up or down based on changing demands, ensuring business continuity and resource optimization.
- Quality Customer Experience: The shared responsibility model ensures top-notch, seamless customer experience as both partners have a vested interest in doing well.
- Expert Management: The performance management of employees rests with the service provider, not the client company. This allows the latter to focus on business-critical functions.
Regular monitoring, communication, and adaptability are key elements in ensuring a positive and sustainable offshore outsourcing experience.
Working Asynchronously with Employees in Different Time Zones
Working asynchronously with employees in different time zones requires intentional strategies to promote effective collaboration and communication.
Here are five ways to successfully work asynchronously in a global team:
- Clear Communication Guidelines: Set clear communication guidelines for response times, channels, and written information. Ensure all team members follow them for effective asynchronous communication.
- Utilize Collaboration Tools: Use collaboration tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or other project management tools to share updates, files, and information in a centralized and accessible space for real-time collaboration and communication.
- Overlapping Work Hours: Schedule important tasks during overlapping work hours of team members in different time zones to enhance real-time communication and ensure critical discussions happen synchronously.
- Document Everything: Store important information in a shared repository to encourage a culture of documentation. This helps team members catch up on important information and reduces the risk of misunderstandings.
- Flexible Work Hours and Results-Oriented Approach: Encourage flexible work hours and prioritize results over sticking to a traditional 9-to-5 schedule. Let team members choose a routine that suits their time zone while meeting objectives. This fosters independence and accommodates varied working hours.
Fostering a sense of inclusivity and acknowledging the diversity of time zones within the team contributes to a positive and collaborative remote work environment.
Industry Trends
The offshoring and outsourcing industry is evolving, shaped by rapid technological advancements, global economic shifts, and the impact of the pandemic.
Here are some key trends to watch:
- Consolidation: As observed in IT service outsourcing, larger companies tend to acquire smaller firms, enabling a wider range of services under one roof to provide a seamless experience to clients.
- Increased Offshoring and Outsourcing: Companies are more inclined to offshore and outsource larger parts of their businesses as they realize these are not core operations that experts in the field can manage.
- Political Backlash: Job loss due to offshoring in developed nations has resulted in growing political backlash. How this will impact offshoring operations remains to be seen.
- Techno-functional Skills Demand: The demand for experts with technical skills and an understanding of business functions is rising. Such skill sets enable easier integration of business operations with technology to deliver more value.
- Ethical and Sustainable Practices: Companies now prefer to work with partners who demonstrate ethical and sustainable practices in alignment with global ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) norms.
Keeping up with industry reports and news is essential to fully comprehend the current dynamics and trends of offshoring and outsourcing. These can change due to global economic conditions, technological advancements, and geopolitical factors.
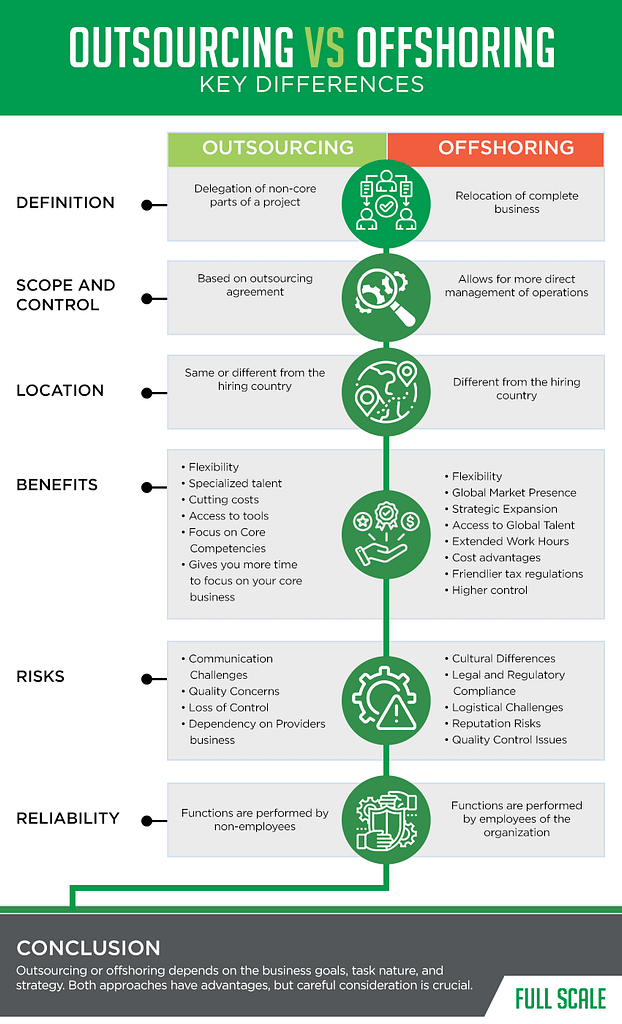
Here’s the summary of the key differences between outsourcing and offshoring:
Full Scale Vouches for Offshoring
Full Scale is in itself run with a team of software developers, web designers, and content creators offshored in the Philippines.
The company’s growth is partly because of the benefits of offshoring that helped it expand by employing well-trained professionals and extending software development and content services to companies such as Gigabook and Stackify.
The company has now helped many startup businesses extend their operations and create their teams for offshoring. As the company grows, the pool of services offered has also expanded.
Ultimately, business success not only lies in the advantages a company can acquire from its engagements but, more importantly, in its ability to make sound decisions regarding what the company needs and requires strategic timing.
At Full Scale, we believe offshoring is a strategic business decision that can greatly contribute to a company’s growth.
We understand that offshoring comes with its unique set of challenges. At Full Scale, we embrace a Managed Offshore Outsourcing model, providing our clients with reduced risk, optimal control, and innovative solutions.
We’re ready to help you navigate your offshoring journey and achieve your business objectives.
Build Your Full Scale Team Today!

Matt Watson is a serial tech entrepreneur who has started four companies and had a nine-figure exit. He was the founder and CTO of VinSolutions, the #1 CRM software used in today’s automotive industry. He has over twenty years of experience working as a tech CTO and building cutting-edge SaaS solutions.
As the CEO of Full Scale, he has helped over 100 tech companies build their software services and development teams. Full Scale specializes in helping tech companies grow by augmenting their in-house teams with software development talent from the Philippines.
Matt hosts Startup Hustle, a top podcast about entrepreneurship with over 6 million downloads. He has a wealth of knowledge about startups and business from his personal experience and from interviewing hundreds of other entrepreneurs.