The Future of Remote Development Tools: Our Predictions
The future of remote development tools has transformed how software teams collaborate across distances.
Adoption of remote development tools has increased by 300% since 2020. This rapid growth stems from necessity but has become a strategic advantage for forward-thinking organizations.
The next generation of remote development tools will transform how distributed engineering teams collaborate, build, and deploy software.
At Full Scale, our experience working with hundreds of distributed teams provides unique insights into this future of remote development evolution.
The Current Remote Development Landscape
The future of remote development is built upon today’s evolving ecosystem of tools and platforms.
Remote development tools continue to mature as organizations embrace distributed work models. The landscape is changing rapidly, and innovations are emerging regularly.
Recent statistics highlight the acceleration in remote development adoption:
- According to Stack Overflow’s 2024 Developer Survey, 78% of developers now use remote development tools daily, up from 52% in 2022 (Stack Overflow, 2024)
- Gartner reports that investment in remote development tools increased by 156% in 2024 compared to pre-pandemic levels (Gartner Research, 2025)
- IDC predicts the remote development tools market will reach $22.7 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 32% (IDC Market Analysis, 2024)
Today’s remote development ecosystem features several powerful platforms that address collaboration needs. These tools enable teams to work cohesively despite geographical separation.
Remote development depends on how these platforms evolve to meet emerging challenges.
Cloud IDEs
Cloud-based Integrated Development Environments represent a significant shift from local development environments. These platforms enable coding directly in browsers with minimal local setup.
Remote development will see these environments becoming increasingly powerful and versatile.
The following table outlines leading Cloud IDE options shaping remote development.
Each platform offers distinct advantages for different team configurations and project requirements.
| Platform | Key Features | Best For | Limitations |
| GitHub Codespaces | Pre-configured environments, GitHub integration, VS Code experience | Enterprise teams using GitHub | Higher cost structure |
| GitPod | Fast startup, ephemeral workspaces, IDE flexibility | Open source contributors, agile teams | Learning curve for configuration |
| CodeSandbox | Instant sharing, collaboration features, templates | Front-end development, rapid prototyping | Less suitable for large-scale projects |
| AWS Cloud9 | AWS integration, pair programming capabilities | AWS-centric development teams | Tied to AWS ecosystem |
Many CTOs at growing FinTech startups have implemented GitHub Codespaces for their distributed teams.
This solution reduced environment setup time from days to minutes and eliminated configuration inconsistencies for offshore development teams working remotely.
Collaboration Tools
Modern development collaboration tools extend beyond basic messaging to enable real-time coding, debugging, and knowledge sharing.
These platforms create virtual spaces for team problem-solving.
The remote development will see these tools becoming more immersive and context-aware.
Remote team productivity tools continue to evolve with powerful new features.
These solutions directly address the challenges of virtual coding environments and support remote engineering.
| Tool | Primary Function | Integration Capabilities | Remote Team Benefits |
| VS Code Live Share | Real-time code collaboration | GitHub, Azure DevOps, Teams | Synchronized debugging, terminal sharing |
| JetBrains Space | Team environment with code review | JetBrains IDEs, Git | Unified team management, automation |
| CodeTogether | Multi-IDE pair programming | Eclipse, VS Code, IntelliJ | Cross-IDE collaboration |
| Tuple | Lightweight pair programming | macOS optimization | Low-latency screen sharing, voice chat |
Product managers at healthcare SaaS companies frequently report that VS Code Live Share reduced debugging sessions from hours to minutes.
This improvement in collaboration tools for developers directly supports remote development by enhancing team velocity.
Infrastructure-as-Code Tools
Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) tools ensure consistent development environments regardless of location.
These solutions minimize “works on my machine” problems for distributed teams. Remote development relies heavily on these tools to provide environment consistency.
The table below highlights key infrastructure tools supporting remote software development trends. These solutions are essential components in the best tools for remote developers’ ecosystem.
| Tool | Environment Parity | Learning Curve | Cloud Provider Support |
| Terraform | High | Moderate | Multi-cloud, provider-agnostic |
| AWS CloudFormation | High | Steep | AWS only |
| Azure Resource Manager | High | Moderate | Azure only |
| Docker/Docker Compose | Moderate | Low | Local and any container service |
Finance directors at e-commerce companies have implemented Terraform to standardize environments for their offshore development tools.
This approach to remote development reduced infrastructure costs while virtually eliminating configuration-related bugs.
Current Pain Points
Despite advancements, distributed engineering teams still face significant challenges with remote development tools. These pain points drive innovation toward future solutions. Remote development must address these core issues to realize its full potential.
Remote-first software development trends and challenges continue to shape tool requirements. These limitations represent opportunities for innovation in remote development.
- Environment inconsistency remains problematic for complex applications with multiple dependencies
- Network latency impacts the experience for team members in regions with limited infrastructure
- Security and compliance requirements create friction in highly regulated industries
- Onboarding remote developers requires a significant time investment
- Context-switching between multiple collaboration tools reduces productivity
Key Driving Forces Shaping the Future
Several technological and organizational trends will shape the evolution of remote development tools. These forces will accelerate change in predictable directions.
Converging innovations are defining remote development.
Understanding these drivers is essential for future-proofing distributed development teams.
Organizations must align their technology strategies with these trends to remain competitive in remote development.
AI and machine learning will dramatically transform how code is written, reviewed, and maintained. By 2026, we expect 75% of code reviews to be AI-assisted, reducing review cycles by 40%. This trend represents a cornerstone of remote development.
AI-Powered Development Assistance
Artificial intelligence rapidly enhances developer productivity through intelligent code completion, error detection, and optimization suggestions. These capabilities will become increasingly sophisticated.
AI will define remote development in software development.
The table below outlines how AI-powered development tools are evolving to support remote work. These capabilities transform how teams collaborate across distances and represent key technologies in remote development.
| AI Capability | Current State | 2025 Prediction | Impact on Remote Teams |
| Code Completion | Context-aware suggestions | Full function generation | 30% faster implementation |
| Automated Testing | Test generation assistance | Autonomous test creation | Reduced QA bottlenecks |
| Code Review | Style checking, basic issue detection | Architectural insights, security analysis | Faster knowledge transfer |
| Documentation | Comment suggestions | Automated documentation generation | Improved asynchronous work |
Many engineering leaders have implemented GitHub Copilot and similar tools for their development teams. Junior developers reached productivity 45% faster while producing more reliable code—demonstrating how remote development enhances team capabilities through AI augmentation.
Security and Compliance Requirements
Growing cybersecurity threats and stringent regulatory requirements will reshape remote development practices. Security will shift from an afterthought to a foundational element of development workflows.
The future of remote development must embrace secure remote coding platforms as standard practice.
The following table examines how different industries approach security in remote development. These requirements significantly influence DevSecOps best practices for remote teams.
| Industry | Key Compliance Concerns | Tool Requirements | Implementation Challenges |
| Financial Services | Data protection, audit trails | Encryption, access controls | Maintaining agility with controls |
| Healthcare | PHI security, HIPAA compliance | Role-based permissions, activity logging | Remote access to sensitive systems |
| Government | Classification levels, sovereignty | Air-gapped solutions, compliance monitoring | Secure collaboration capabilities |
| E-commerce | Payment data, consumer privacy | PCI compliance tools, secure coding enforcement | Balancing innovation with security |
Talent acquisition managers at financial services firms have implemented secure development environments with advanced compliance monitoring.
This approach to remote development reduced audit preparation time while maintaining remote work flexibility for global teams.
Immersive Collaboration Experiences
The future of remote development involves more immersive, context-rich collaboration beyond simple screen sharing.
Teams will interact in virtual spaces that simulate the benefits of physical collaboration. These emerging technologies represent how remote development tools are evolving in 2025.
The table below highlights immersive technologies enhancing remote development.
These solutions address fundamental challenges in managing a remote engineering team effectively.
| Technology | Collaboration Enhancement | Adoption Timeline | Remote Development Impact |
| Spatial Audio | Location-based sound in virtual workspaces | 2023-2024 | Enhanced team awareness |
| 3D Visualization | Interactive architecture and data modeling | 2024-2025 | Better system understanding |
| VR Code Spaces | Immersive development environments | 2025-2026 | Enhanced pair programming |
| Digital Twins | Virtual replicas of development environments | 2026-2027 | Improved troubleshooting |
Development team leaders report that immersive collaborative debugging reduced feature development time by 35%.
This benefit of remote development allows teams to solve complex issues faster through shared virtual environments and enhanced communication.
Edge Computing Impact
The rise of edge computing is changing application architectures and development workflows. Teams must adapt to new paradigms for testing, deployment, and monitoring.
The future of remote development increasingly intersects with edge computing requirements.
This table examines how edge computing impacts remote software engineering practices. These factors directly influence remote development tool requirements and capabilities.
| Edge Factor | Development Implications | Tool Evolution | Remote Team Adaptation |
| Latency Requirements | Local testing of time-sensitive features | Edge emulation tools | Distributed testing frameworks |
| Connectivity Constraints | Offline-first development approaches | Sync/conflict resolution tools | Asynchronous workflow patterns |
| Device Diversity | Cross-platform testing complexity | Device simulation platforms | Specialized QA processes |
| Data Sovereignty | Region-specific deployment considerations | Multi-region deployment orchestration | Compliance-aware CI/CD |
Five Bold Predictions for Remote Development Tools
The next generation of remote development tools will transform distributed software creation. These predictions represent our vision for remote development.
Each forecast reflects emerging technologies that will reshape how teams collaborate across distances.
These five key innovations will define the future of remote development.
Organizations that adopt these technologies early will gain significant advantages in team productivity and output quality.
1. AI Pair Programmers Will Become Standard
AI pair programming will evolve from helpful suggestions to active collaboration partners. These systems will participate in development as team members with specialized expertise.
Remote development will see AI become integral to every developer’s workflow.
The following table outlines the evolution of AI in software development for remote teams. These capabilities represent remote development’s most transformative potential.
| AI Pair Programming Feature | Timeline | Productivity Impact | Adoption Barriers |
| Context-aware code generation | 2024-2025 | 25-30% faster implementation | Trust in generated code |
| Architectural guidance | 2025-2026 | 15-20% better design decisions | Integration with existing processes |
| Automated refactoring | 2026-2027 | 40% reduction in technical debt | Change management resistance |
| Knowledge base integration | 2027-2028 | 50% faster onboarding | Initial training investment |
Companies like GitHub (Copilot), OpenAI (Code Interpreter), and Tabnine are pioneering these capabilities.
Their current offerings will mature into comprehensive AI programming partners that define remote development for distributed teams.
Technical leaders predict their teams’ productivity will increase by 40% with advanced AI assistance.
This capability will be particularly valuable for distributed teams where knowledge sharing is challenging—a key concern in remote development.
2. Development Environments Will Become Fully Portable
Future development environments will achieve complete portability across devices and platforms.
Developers will access identical environments from any device with minimal configuration.
Eliminating environmental inconsistencies is crucial for remote development.
This table examines how portable environments will enhance remote development tools. These capabilities directly address key limitations in current virtual development environments.
| Portability Feature | Implementation Mechanism | Remote Work Benefit | Time to Mainstream |
| Universal workspace access | WebAssembly-powered IDEs | Device independence | 1-2 years |
| State preservation | Continuous synchronization | Seamless context switching | 2-3 years |
| Cross-device continuation | Environment mirroring | Flexible work locations | 2-3 years |
| Offline capability | Local-first architecture | Resilience to connectivity issues | 3-4 years |
Technologies enabling this transition include WebAssembly, Git-based environment definitions, and containerization advancements.
These technologies eliminate environmental inconsistencies that have historically limited remote development.
Financial decision-makers appreciate how portable environments reduce infrastructure costs in remote development.
Their teams typically see significant reductions in computing expenses while improving developer satisfaction through hybrid work software solutions.
3. AR/VR Collaborative Coding Spaces
Augmented and virtual reality will transform remote collaboration beyond screen sharing. Teams will work in shared spatial environments that mirror physical collaboration benefits.
Remote development will increasingly incorporate immersive technologies.
The following table outlines emerging AR/VR capabilities shaping the future of remote development. These technologies represent emerging tech for remote software collaboration at its most innovative.
| Feature | Technology Enabler | Collaboration Improvement | Adoption Timeline |
| Spatial code visualization | 3D rendering engines | 30% improved comprehension | 2025-2026 |
| Virtual whiteboards | Hand tracking, spatial mapping | 40% better design sessions | 2024-2025 |
| Avatar-based presence | Motion capture, spatial audio | Enhanced team cohesion | 2024-2025 |
| Immersive debugging | System visualization tools | 28% faster bug resolution | 2026-2027 |
Early adopters using prototype systems have reported 28% faster bug resolution through immersive collaboration.
Companies like Meta, Microsoft, and specialized startups like Spatiallitics are developing these platforms that will define remote development.
Engineering leaders believe AR/VR environments will be mainstream for enterprise development by 2027.
Companies building complex systems will adopt these tools first, establishing new standards for remote development.
4. Hybrid Cloud-Edge Development Frameworks
Development frameworks will evolve to support hybrid cloud-edge architectures seamlessly.
These frameworks will simplify building applications that span centralized and distributed infrastructure.
The future of remote development increasingly requires edge-aware tooling.
This table highlights how hybrid frameworks will transform remote software development trends. These capabilities address essential requirements for remote engineering.
| Framework Feature | Technical Approach | Development Benefit | Maturity Timeline |
| Unified programming model | Abstraction layers, smart SDKs | Simplified distributed architecture | 2024-2025 |
| Automated partitioning | Static analysis, deployment optimization | Optimal code distribution | 2025-2026 |
| Latency simulation | Network condition emulation | Realistic local testing | 2024-2025 |
| Multi-region CI/CD | Orchestrated deployment pipelines | Consistent global delivery | 2025-2026 |
Financial services applications requiring ultra-low latency will drive the adoption of these frameworks in remote development.
Trading platforms have already seen a 60% latency reduction through specialized edge deployment technologies for remote software engineering.
Product managers value how these frameworks simplify creating responsive applications in remote development.
Their healthcare applications achieved 40% better response times after implementing edge components through cloud-based development tools.
5. Unified DevSecOps Platforms for Distributed Teams
Security will shift from checkpoint validation to continuous integration throughout the development process.
Unified platforms will seamlessly incorporate security into every stage. Remote development must prioritize security without compromising productivity.
The table below examines how DevOps for remote teams is evolving to integrate security. These capabilities represent remote development’s approach to managing risk.
| Platform Capability | Implementation Method | Distributed Team Benefit | Expected Rollout |
| Security as code | Policy-as-code, compliance automation | Consistent governance | 2024-2025 |
| Automated vulnerability remediation | AI-powered fix generation | Reduced security backlog | 2025-2026 |
| Continuous compliance monitoring | Regulatory mapping engines | Simplified audit processes | 2024-2025 |
| Shift-left security testing | Pre-commit hooks, IDE integration | Earlier issue detection | 2023-2024 |
Human resources professionals benefit from standardized security onboarding in these platforms.
New remote developers reach full productivity 60% faster with built-in security guidance—a key advantage in remote development.
Financial leaders appreciate how these platforms reduce security-related delays in remote development.
Their teams typically see significant reductions in deployment delays due to integrated security processes for scalable engineering teams.
Preparing Your Team for These Changes
Organizations must strategically prepare for technological shifts in remote development. This preparation includes skills development, tool evaluation, and process adaptation.
Successful teams proactively implement changes rather than reacting to industry pressure.
Remote development requires careful planning and systematic implementation.
These strategies ensure teams can maximize the benefits of emerging technologies while effectively managing transition challenges.
Skills Assessment
Future remote development requires specific technical and collaboration skills. Teams should prioritize developing these capabilities to remain competitive.
Remote development demands ongoing learning and adaptation.
The following table outlines key skills needed for remote development. These capabilities represent areas where proactive training delivers significant advantages.
| Skill Category | Critical Capabilities | Training Approach | Priority Level |
| Cloud Architecture | Distributed systems design, microservices | Certification programs, hands-on projects | High |
| AI/ML Fundamentals | Prompt engineering, model evaluation | Online courses, guided practice | Medium |
| DevSecOps | Security automation, compliance integration | Workshops, security certifications | High |
| Immersive Technologies | AR/VR development basics | Introductory courses, experimental projects | Low-Medium |
| Edge Computing | Edge architecture patterns, optimization | Technical workshops, case studies | Medium |
Engineering leaders have implemented skills matrices for their teams, preparing for remote development. This approach identifies critical capability gaps and creates targeted development plans for the best AI tools for remote software engineers.
Adoption Roadmap
A phased approach to implementing next-generation tools ensures successful integration with minimal disruption.
This roadmap provides a structured transition timeline for remote development. Careful planning prevents productivity disruptions during implementation.
The table below outlines a strategic approach to adopting future remote development tools. This framework helps organizations manage change systematically while maximizing benefits.
| Phase | Timeline | Focus Areas | Success Metrics |
| Assessment | 1-2 months | Current tools evaluation, gap analysis | Comprehensive inventory, prioritized needs |
| Pilot Implementation | 2-4 months | Limited testing of selected tools | Developer satisfaction, productivity metrics |
| Initial Deployment | 3-6 months | Core team adoption, workflow integration | Adoption rate, issue resolution time |
| Full Rollout | 6-12 months | Organization-wide implementation | Team velocity, quality indicators |
| Optimization | Ongoing | Continuous improvement, capability expansion | ROI metrics, competitive advantage |
The following diagram illustrates a recommended adoption roadmap for remote development tools.
This visual guide outlines each phase, from initial assessment to ongoing optimization, displaying each stage’s progression and key activities.
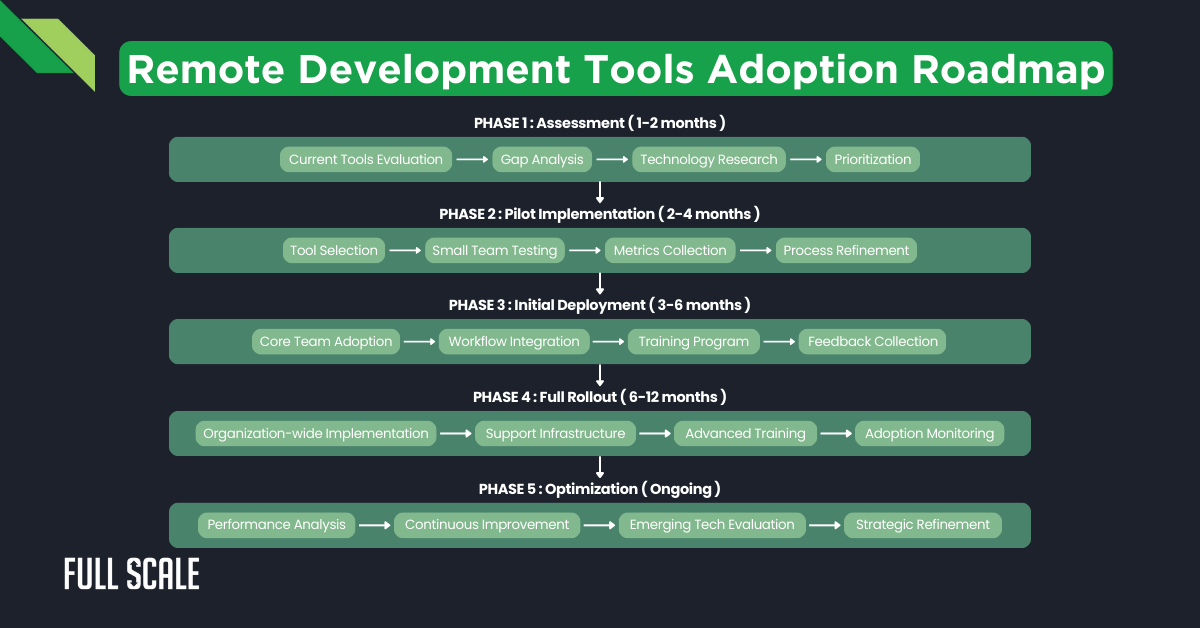
Product leaders recommend starting with tools that solve immediate pain points in remote development. Many teams begin with collaboration tools for developers before moving to more advanced technologies to enhance developer productivity in remote settings.
ROI Calculation Framework
Investment in new development tools requires clear financial justification. This framework helps quantify benefits against implementation costs for remote development.
Demonstrating ROI secures leadership support for technology investments.
The following table provides a framework for measuring the financial impact of remote development tools.
These metrics help justify investments in the future of remote development technologies.
| Benefit Category | Measurement Approach | Typical Impact Range | Data Collection Method |
| Developer Productivity | Code commit velocity, feature completion time | 20-35% improvement | Automated metrics, surveys |
| Quality Improvement | Defect reduction, test coverage increase | 15-30% improvement | QA metrics, customer reports |
| Time-to-Market | Release cycle reduction, feature delivery time | 25-40% improvement | Project tracking systems |
| Team Satisfaction | Retention improvement, positive feedback | 10-25% improvement | Engagement surveys, turnover data |
| Cost Reduction | Infrastructure savings, reduced overhead | 15-40% reduction | Financial analysis, utilization data |
Finance directors have created comprehensive ROI calculators for remote development tools. This approach secured executive buy-in for significant infrastructure investments in remote development.
Training Strategies
Effective training ensures team members can maximize the benefits of the new tool. Different approaches work best for different technologies in remote development.
Strategic training minimizes productivity dips during technology transitions.
This table outlines effective approaches to training for remote development. These strategies ensure teams can fully leverage new capabilities in remote team productivity tools.
| Training Approach | Best For | Implementation Complexity | Time Investment |
| Pair Programming | Tool-specific techniques | Low | Moderate |
| Documentation & Self-Paced | Standard technologies | Low | Variable |
| Internal Workshops | Team-wide adoption | Moderate | High initially, low ongoing |
| External Training | Specialized new technologies | Moderate-High | High |
| Certification Programs | Core strategic capabilities | High | High |
HR professionals have implemented training rotation systems for new remote development tools.
This approach creates internal experts who support wider team adoption—a critical success factor in the future of remote development.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
Despite promising advancements, organizations must address several challenges when adopting next-generation remote development tools.
These limitations require strategic planning and mitigation. The future of remote development involves balancing technological possibilities with practical constraints.
Remote-first software development trends and challenges include several potential barriers to adoption.
Recognizing these issues allows organizations to develop effective strategies for the future of remote development.
Connectivity Requirements
Advanced collaboration tools demand reliable, high-bandwidth connections.
This requirement creates access barriers in some regions where the future of remote development might otherwise flourish.
Connectivity limitations remain a significant constraint for global teams.
The table below examines connectivity challenges affecting the future of remote development. These issues require specific technical and organizational solutions.
| Challenge | Impact | Mitigation Strategy | Implementation Complexity |
| Bandwidth Constraints | Degraded collaboration experience | Adaptive quality settings, offline modes | Moderate |
| Reliability Issues | Work disruption, synchronization problems | Resilient design, conflict resolution | High |
| Regional Disparities | Uneven team experience | Infrastructure investment, proximate hub offices | High |
| Cost Implications | Expense burden on remote workers | Stipend programs, corporate connectivity solutions | Low-Moderate |
Engineering leaders have implemented hybrid solutions with offline capabilities for the future of remote development.
This approach enabled team members in regions with connectivity challenges to remain productive while using cloud-based collaboration tools for developers.
Security and Data Sovereignty
Advanced remote development tools must navigate complex security requirements and regional data regulations.
These considerations may limit deployment options in the future of remote development. Security and compliance demands vary significantly by industry and region.
The following table outlines security considerations for the future of remote development. These factors influence secure remote coding platform’s design and implementation.
| Concern | Regulatory Impact | Technical Requirements | Industry Sensitivity |
| Data Residency | Storage location restrictions | Region-specific deployment | High (Financial, Healthcare) |
| Information Classification | Handling requirements | Access controls, encryption | High (Government, Defense) |
| Cross-Border Transfer | Transfer limitations | Data minimization, tokenization | Medium-High (Multiple) |
| Audit Requirements | Compliance demonstration | Comprehensive logging, attestation | Medium (Regulated Industries) |
Financial leaders have implemented data classification and region-specific deployment policies for the future of remote development.
This approach ensured regulatory compliance without compromising developer experience across distributed software teams.
Cultural Resistance
Adopting new development methodologies often faces cultural resistance. Overcoming this resistance requires change management strategies aligned with the future of remote development.
Organizational culture significantly influences technology adoption success.
This table examines types of resistance that might impede the future of remote development.
Recognizing these patterns helps organizations develop effective change management strategies.
| Resistance Type | Common Manifestations | Mitigation Approach | Success Factors |
| Process Attachment | “Our current way works fine” | Incremental change, clear benefits | Leadership support, demonstrated value |
| Tool Familiarity | Preference for known environments | Transition periods, hybrid approaches | Comprehensive training, peer champions |
| Collaboration Styles | Discomfort with transparent processes | Graduated visibility, feedback mechanisms | Culture building, team agreements |
| Performance Concerns | Fears about monitoring | Clear measurement policies, focus on outcomes | Trust building, fair evaluation metrics |
Product managers have created change management plans centered on developer experience for the future of remote development.
This approach highlighted benefits resonating with technical teams while addressing concerns about managing a remote engineering team effectively.
Cost Considerations
Implementing next-generation tools requires significant investment. Organizations must balance immediate costs against long-term benefits in the future of remote development.
Financial considerations often determine implementation timelines and scope.
The table below examines cost factors affecting the future of remote development adoption. These considerations influence budget planning and resource allocation.
| Cost Category | Impact Scale | ROI Timeline | Optimization Strategies |
| Licensing/Subscription | Medium-High | 6-18 months | Tiered implementation, usage-based plans |
| Infrastructure | Medium-High | 12-24 months | Gradual migration, hybrid approaches |
| Training/Onboarding | Medium | 3-9 months | Train-the-trainer models, self-service resources |
| Integration | Medium | 6-12 months | Phased connectivity, API-first approach |
| Support/Maintenance | Low-Medium | Ongoing | Internal expertise development, community engagement |
HR directors have developed phased investment plans aligned with measurable outcomes for the future of remote development.
This approach secured ongoing funding by demonstrating incremental ROI for hybrid work software solutions.
Our Strategic Recommendations
Based on our experience with hundreds of distributed teams, Full Scale recommends a structured approach to adopting next-generation remote development tools.
These strategies maximize benefits while minimizing disruption.
The future of remote development requires balancing innovation with operational stability.
Our recommendations reflect insights from working with diverse organizations exploring the future of remote development. These approaches have consistently delivered positive outcomes for teams transitioning to more advanced remote collaboration models.
Short-Term Actions (Next 6 Months)
Organizations should take immediate steps to prepare for technological shifts while addressing current pain points. These actions create momentum toward the future of remote development. Quick wins build organizational support for larger initiatives.
The table below outlines high-impact, short-term actions supporting the future of remote development. These initiatives deliver immediate benefits while building foundations for longer-term transformation.
| Action | Implementation Approach | Expected Outcome | Resource Requirements |
| Evaluate AI coding assistants | Limited pilot with measurable metrics | 15-25% productivity increase | Low (subscription costs) |
| Standardize environment definitions | Container-based development environments | 40-60% reduction in configuration issues | Medium (DevOps time) |
| Implement asynchronous code review | Structured review tools with templates | 30-50% faster review cycles | Low (process changes) |
| Enhance security scanning | IDE-integrated and CI/CD security tools | 20-35% earlier vulnerability detection | Medium (tools, configuration) |
| Assess collaboration friction points | Developer surveys, workflow analysis | Prioritized improvement roadmap | Low (analysis time) |
Financial decision-makers recommend starting with tools that offer immediate ROI in the future of remote development.
Many teams begin with AI coding assistants that show positive returns within weeks—establishing credibility for future investments.
Medium-Term Preparation (6-18 Months)
Medium-term investments should focus on competitive differentiation and systematic improvements to development processes.
These initiatives strengthen the foundation for the future of remote development.
Strategic investments in this timeframe position organizations for long-term advantage.
The following table outlines medium-term investment areas for the future of remote development.
These capabilities deliver substantial competitive advantages for distributed software teams.
| Investment Area | Implementation Strategy | Competitive Advantage | Organization Impact |
| Cloud-native development platforms | Unified environment standardization | Faster onboarding, consistent quality | High (developer experience) |
| Advanced collaboration spaces | Virtual workspace implementation | Enhanced team cohesion, problem-solving | Medium-High (innovation speed) |
| Security automation pipeline | DevSecOps platform integration | Reduced vulnerabilities, compliance efficiency | High (risk reduction) |
| Edge development frameworks | Hybrid architecture patterns, testing tools | Performance advantages, market responsiveness | Medium (architecture evolution) |
| Knowledge management systems | Automated documentation, contextual assistance | Faster knowledge transfer, reduced dependencies | Medium (organizational learning) |
Technical leaders prioritize investing in cloud-native development platforms for the future of remote development. This approach creates a foundation for more advanced capabilities while delivering immediate productivity benefits for offshore development tools.
Long-Term Vision Alignment (18+ Months)
Long-term planning should position organizations to lead technological adoption while maintaining strategic flexibility.
This vision guides incremental decisions toward the future of remote development.
Forward-looking organizations prepare for emerging technologies before they become mainstream.
This table outlines strategic focus areas for long-term leadership in the future of remote development. These priorities position organizations at the forefront of industry evolution.
| Strategic Focus | Positioning Approach | Leadership Opportunity | Industry Impact |
| AI-augmented development | Comprehensive AI integration strategy | 30-50% productivity advantage | Transformative |
| Immersive collaboration platforms | Early adoption partnerships, feature influence | Enhanced distributed innovation capability | Significant |
| Edge computing excellence | Specialized architecture expertise, tooling | Performance differentiation, new use cases | Significant |
| Security-driven development | Zero-trust implementation, compliance automation | Reduced breach risk, faster certification | Moderate-High |
| Global talent enablement | Anywhere-work technology stack | Access to premium global talent | Transformative |
Product leaders suggest creating centers of excellence for critical technologies supporting the future of remote development.
These focused teams accelerate adoption across the organization while future-proofing distributed development teams against technological disruption.
The Future of Remote Development: Embracing the Next Evolution
The future of remote development tools will fundamentally transform how distributed engineering teams build software.
AI assistance, immersive collaboration, portable environments, edge computing frameworks, and unified security platforms will create competitive advantages for early adopters in the future of remote development.
Let’s recap our key predictions for the future of remote development:
- AI Pair Programmers as Standard – By 2026, AI-powered coding assistants will evolve from suggestion tools to full collaboration partners, increasing developer productivity by 25-40%.
- Fully Portable Development Environments – Within 1-3 years, developers will access identical environments from any device with complete state preservation and offline capabilities.
- AR/VR Collaborative Coding Spaces – Immersive technologies will transform remote collaboration by 2027, enabling spatial code visualization and virtual workspaces that improve bug resolution by 28%.
- Hybrid Cloud-Edge Development Frameworks – New development frameworks will simplify building applications that span centralized and distributed infrastructure, reducing latency by up to 60%.
- Unified DevSecOps Platforms – Security will shift from checkpoint validation to continuous integration, with automated vulnerability remediation reducing deployment delays by 35%.
Organizations that strategically implement these technologies will enjoy significant benefits in the future of remote development.
These advantages include enhanced developer productivity, improved software quality, accelerated time-to-market, and access to global talent pools through advanced remote development tools.
Streamline Remote Development with Full Scale
Implementing next-generation remote development tools requires expertise and experience in distributed software teams.
At Full Scale, we specialize in helping businesses build and manage remote development teams equipped with cutting-edge tools that embrace the future of remote development.
Why Choose Full Scale for Your Remote Development Future:
- Future-Ready Development Teams: Our skilled developers are trained in the latest remote development tools and emerging technologies shaping the future of distributed work.
- Seamless Global Collaboration: Our virtual coding environments and collaboration platforms integrate effortlessly with your existing processes, ensuring smooth teamwork across any distance.
- Strategic Technology Roadmaps: We help you navigate the future of remote engineering with tailored adoption strategies for AI-powered development tools and immersive collaboration solutions.
- Scalable Remote Operations: Focus on strategic goals while we help you implement secure remote coding platforms and cloud-based development tools that position your organization for future success.
Full Scale Services for Remote Development Excellence:
- Software Development Services: Build scalable, high-quality applications with our expert remote development teams.
- Software Testing Services: Ensure flawless performance with comprehensive QA and testing capabilities.
- App Development Services: Create responsive mobile and web applications optimized for global users.
- UX Design Services: Craft intuitive user experiences that work seamlessly across all devices.
- Staff Augmentation Services: Expand your team with specialized talent equipped with the latest remote development tools.
Don’t let the rapidly evolving remote development landscape leave you behind.
Schedule a free consultation today to discover how Full Scale can transform your distributed software teams and help you capitalize on the future of remote development.
Accelerate Your Remote Development
FAQs: The Future of Remote Development
What are the most significant challenges in the future of remote development?
Remote development faces several key challenges, including connectivity limitations in regions with poor infrastructure, security and compliance concerns across different jurisdictions, cultural resistance to new collaboration methodologies, and initial implementation costs. Organizations must develop specific strategies to address these barriers while adopting cloud-based development tools and secure remote coding platforms.
How will AI impact remote software development teams?
AI will fundamentally transform remote development by automating routine coding tasks, enhancing code reviews, generating documentation, and eventually functioning as collaborative pair programmers. The best AI tools for remote software engineers will reduce implementation time by 25-40%, accelerate onboarding processes, and help bridge knowledge gaps across distributed software teams working in different time zones.
What skills should developers focus on for the future of remote development?
Developers preparing for remote development should prioritize cloud architecture expertise, AI/ML fundamentals, DevSecOps practices, and distributed system design. Remote software engineering increasingly requires proficiency with virtual development environments and remote team productivity tools. Skills in collaborative asynchronous workflows and security-first coding practices will become essential in hybrid work software solutions.
How can companies measure ROI from investments in remote development tools?
Companies can measure ROI in remote development through specific metrics like code commit velocity, feature completion time, defect reduction rates, and release cycle acceleration. Successful organizations track productivity improvements (typically 20-35%), quality enhancements (15-30%), and time-to-market reduction (25-40%) to justify investments in advanced remote development tools and offshore development team capabilities.
When should organizations begin transitioning to next-generation remote development tools?
Organizations should begin their remote development journey immediately with a phased approach. Start by evaluating current pain points, implementing AI coding assistants, standardizing environments, and enhancing collaboration processes. Create a strategic roadmap spanning 18-24 months that balances immediate productivity gains with long-term strategic advantages for scalable engineering teams and future-proofing distributed development teams.
How can Full Scale help organizations implement remote development?
Full Scale accelerates your journey into remote development through our comprehensive suite of specialized services. Our Software Development Services create scalable applications with distributed teams using the latest cloud-based development tools. Through our Software Testing and QA capabilities, we ensure your remote development workflow produces high-quality outcomes. Our UX Design Services optimize user experiences across all platforms, while our Staff Augmentation Services provide immediate access to developers skilled in AI-powered development tools and virtual coding environments. Full Scale’s expertise in managing offshore development teams enables seamless implementation of next-generation remote collaboration tools.



