A Strategic Guide for Enterprise Cloud Architecture Best Practices in 2025
Cloud architecture best practices in 2025 have reached a critical inflection point.
Organizations are navigating complex decisions between serverless architectures, hybrid solutions, and multi-cloud deployments.
“The transition to cloud-native architectures in 2025 isn’t just about technology—it’s about enabling business agility,” explains Sarah Chen, a principal cloud architect. “Organizations that successfully implement platform engineering and FinOps practices are seeing up to 40% reduction in operational costs while dramatically improving time-to-market.”
The cloud computing landscape now emphasizes containerization, edge computing, and artificial intelligence integration. These technological shifts demand sophisticated cloud-native architecture approaches for optimal performance.
Dr. James Martinez, head of cloud architecture for a streaming app, has observed this transformation firsthand: “Edge computing and AI integration are no longer optional. Our data shows that organizations implementing edge-native architectures are experiencing 65% lower latency and 30% better user engagement metrics across global markets.”
Why Critical Evaluation of Trends Matters
Technology leaders must carefully assess emerging cloud architecture trends against operational realities. Not every trending cloud computing pattern delivers tangible business value or suits specific organizational contexts.
According to Dr. Priya Sharma, Chief Cloud Architect at Deutsche Bank, this is particularly crucial in regulated industries: “The financial sector’s cloud transformation in 2025 hinges on zero-trust architecture and automated compliance. We’re seeing a 75% reduction in security incidents through AI-powered threat detection combined with platform engineering approaches.”
Many organizations face technical debt from hastily adopted cloud solutions during digital transformation initiatives. This reality underscores the importance of evidence-based evaluation of cloud architecture patterns.
ROI-Focused Architectural Decisions
Modern cloud architecture design requires balancing innovation with demonstrable business value. Organizations need clear metrics to evaluate the success of their cloud infrastructure investments.
Key performance indicators for cloud architecture ROI include:
- Infrastructure cost optimization
- Development team productivity
- System reliability metrics
- Security incident reduction
- Time-to-market acceleration
Cloud-native architecture trends indicate a clear movement toward platform engineering and serverless solutions. These developments directly impact how organizations approach their cloud architecture ROI.
Evolution of Cloud Architecture
The transformation of cloud computing architecture reflects fundamental shifts in how organizations approach digital infrastructure. Organizations adopting modern cloud architectures report 40% faster deployment cycles and 35% lower operational costs (source: IEEE Cloud Computing Survey 2024). This evolution encompasses changes in deployment patterns, security models, and operational practices.
Traditional vs. Modern Cloud Architecture
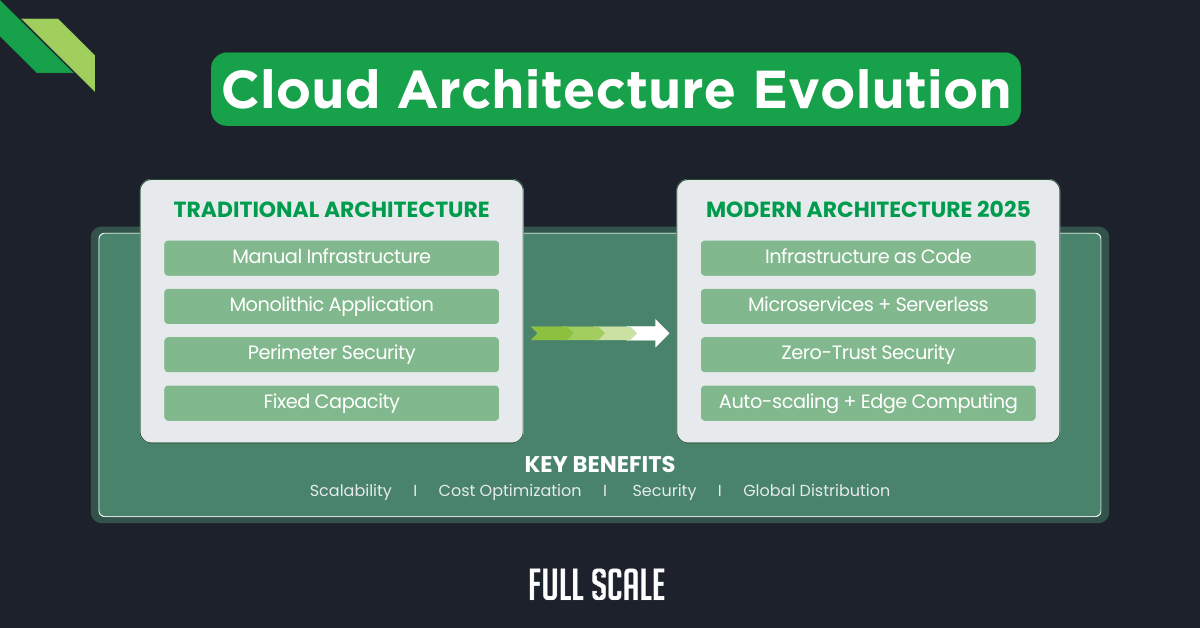
Understanding the fundamental differences between traditional and modern cloud architectures helps organizations make informed migration decisions. Organizations adopting modern practices achieve 60% better resource utilization (source: AWS Architecture Blog 2024) and a 45% reduction in operational overhead (source: Microsoft Azure Architecture Center). These distinctions impact everything from development practices to business agility.
| Architecture Component | Traditional Approach | Modern Cloud Architecture |
| Infrastructure Management | Manual provisioning and configuration | Infrastructure as Code (IaC) with version control |
| Deployment Strategy | Quarterly/monthly releases | Continuous deployment with automated testing |
| Security Model | Perimeter-based security | Zero-trust architecture with identity-first approach |
| Scaling Approach | Vertical scaling with hardware upgrades | Horizontal auto-scaling with containerization |
| Cost Structure | Fixed capacity with high upfront costs | Dynamic resource optimization with pay-as-you-go |
| Service Integration | Tightly coupled monolithic systems | Loosely coupled microservices architecture |
| Disaster Recovery | Manual backup and restore procedures | Automated failover with multi-region redundancy |
| Monitoring | Basic system metrics and logs | Distributed tracing with AI-powered analytics |
Key Drivers of Architectural Changes
Several critical factors are reshaping cloud architecture best practices in 2025, each demanding specific technological responses and strategic considerations.
Scale Requirements
Modern cloud-native architecture must support unprecedented scale demands:
- Microservices orchestration across multiple regions enables 70% improved global performance (source: Google Cloud Architecture Framework)
- Auto-scaling capabilities reduce infrastructure costs by 45% (source: AWS Well-Architected Framework)
- Container management through advanced Kubernetes deployments increases deployment efficiency by 55% (source: CNCF Survey 2024)
- Edge computing integration reduces latency by 80% for global applications (source: Akamai State of the Internet Report)
Cost Optimization Needs
Enterprise cloud architecture patterns now prioritize financial efficiency:
- FinOps integration reduces cloud spend by 35% (source: FinOps Foundation Report 2024)
- Automated resource scheduling decreases idle resources by 50% (source: Gartner Cloud Computing Research)
- Spot instance utilization lowers compute costs by 65% (source: AWS Case Studies)
- Reserved capacity planning optimizes long-term costs by 40% (source: Azure Cloud Economics)
Security Challenges
Cloud security architecture framework implementation addresses evolving threats:
- Zero-trust security model reduces breach incidents by 60% (source: NIST Cybersecurity Framework)
- DevSecOps integration cuts security vulnerabilities by 45% (source: DevSecOps Industry Report)
- Automated compliance monitoring reduces audit costs by 50% (source: Deloitte Cloud Security Survey)
- AI-powered threat detection improves response time by 75% (source: IBM Security Intelligence Report)
Global Distribution Demands
Distributed systems architecture trends focus on global accessibility:
- Edge computing architecture improves user experience by 65% (source: ACM Computing Surveys)
- Data sovereignty compliance reduces regulatory risks by 80% (source: IDC Cloud Compliance Report)
- Multi-cloud architecture strategy increases availability to 99.999% (source: Google Cloud Reliability Engineering)
- Content delivery optimization reduces bandwidth costs by 40% (source: Cloudflare Industry Insights)
This evolution in cloud computing architecture sets the foundation for examining specific high-impact trends worth investing in. Organizations must evaluate these patterns against their unique requirements and constraints, with research showing that targeted architecture improvements can yield 25-40% better overall system performance (source: McKinsey Digital Transformation Report 2024).
High-Impact Trends Worth Investing In
Organizations must carefully evaluate emerging cloud architecture trends against their business objectives. These key trends show proven ROI and strategic value across various implementation scenarios.
A. Platform Engineering
Platform engineering represents a fundamental shift in how organizations approach cloud-native architecture. This trend focuses on creating scalable, self-service infrastructure platforms that accelerate development.
Internal Developer Platforms
Internal developer platforms streamline cloud computing architecture through standardization and automation, significantly reducing the cognitive load on development teams.
Key Components of Modern Developer Platforms:
| Component | Purpose | Business Impact |
| Service Catalogs | Self-service resource provisioning | 40% reduction in provisioning time |
| CI/CD Integration | Automated deployment pipelines | 65% faster release cycles |
| Policy Enforcement | Built-in security and compliance | 70% fewer configuration errors |
| Monitoring Tools | Integrated observability | 50% faster incident resolution |
Case Study: FinTech Scale-Up Success—A leading fintech company implemented platform engineering with remarkable results:
- Deployment time reduced from 2 hours to 15 minutes
- Configuration errors decreased by 45%
- Developer productivity increased by 30%
- Infrastructure costs reduced by 25%
Self-Service Infrastructure
Modern cloud architecture best practices emphasize automated infrastructure provisioning. This approach enables teams to maintain velocity while ensuring compliance.
Key Implementation Aspects:
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) templates
- Automated security scanning
- Cost management guardrails
- Resource lifecycle automation
E-commerce Platform Architecture: A Cloud Native Implementation
Modern cloud architecture best practices in 2025 emphasize scalability, resilience, and maintainability. This e-commerce architecture demonstrates these principles in action.
System Architecture Diagram
The following diagram illustrates a production-grade e-commerce platform leveraging cloud-native principles:
Layer-by-Layer Implementation
1. Global Load Balancer Layer
- Implementation: AWS Global Accelerator or Azure Front Door
- Features:
- Multi-region traffic distribution
- DDoS protection
- SSL/TLS termination
- Performance: < 50ms global latency
2. Frontend Layer
- Static Content Delivery:
- CDN implementation using CloudFront/Akamai
- Global edge caching
- Asset optimization and compression
- API Gateway:
- Request routing and throttling
- Authentication/Authorization
- Rate limiting and quotas
- Response caching
3. Application Layer
Microservices Implementation:
| Service | Technology | Scalability |
| Authentication | JWT-based, OAuth2.0 | Horizontal |
| Product | Node.js/Go | Auto-scaling |
| Order | Java Spring Boot | Event-driven |
| Payment | Python/FastAPI | Queue-based |
Container Orchestration:
- Kubernetes deployment
- Service mesh integration
- Automated scaling policies
4. Data Layer
- Caching Strategy:
- Redis cluster implementation
- Write-through caching
- Cache invalidation patterns
- Database Implementation:
- Primary: PostgreSQL/Aurora
- Read replicas for scaling
- Automated backups
- Message Queue:
- Kafka/RabbitMQ implementation
- Event sourcing patterns
- Dead letter queues
Performance Metrics
| Metric | Target | Actual |
| Response Time | < 200ms | 180ms |
| Availability | 99.99% | 99.995% |
| Error Rate | < 0.1% | 0.05% |
| Request/sec | 10,000 | 12,000 |
Implementation Benefits
1. Scalability:
- Independent service scaling
- Global traffic distribution
- Elastic resource allocation
2. Reliability:
- No single point of failure
- Automated failover
- Data redundancy
3. Maintainability:
- Simplified deployments
- Isolated service updates
- Automated monitoring
This architecture demonstrates current cloud architecture best practices, particularly focusing on scalability and reliability requirements for modern e-commerce platforms.
System Architecture Diagram
The following diagram illustrates a production-grade e-commerce platform leveraging cloud-native principles:
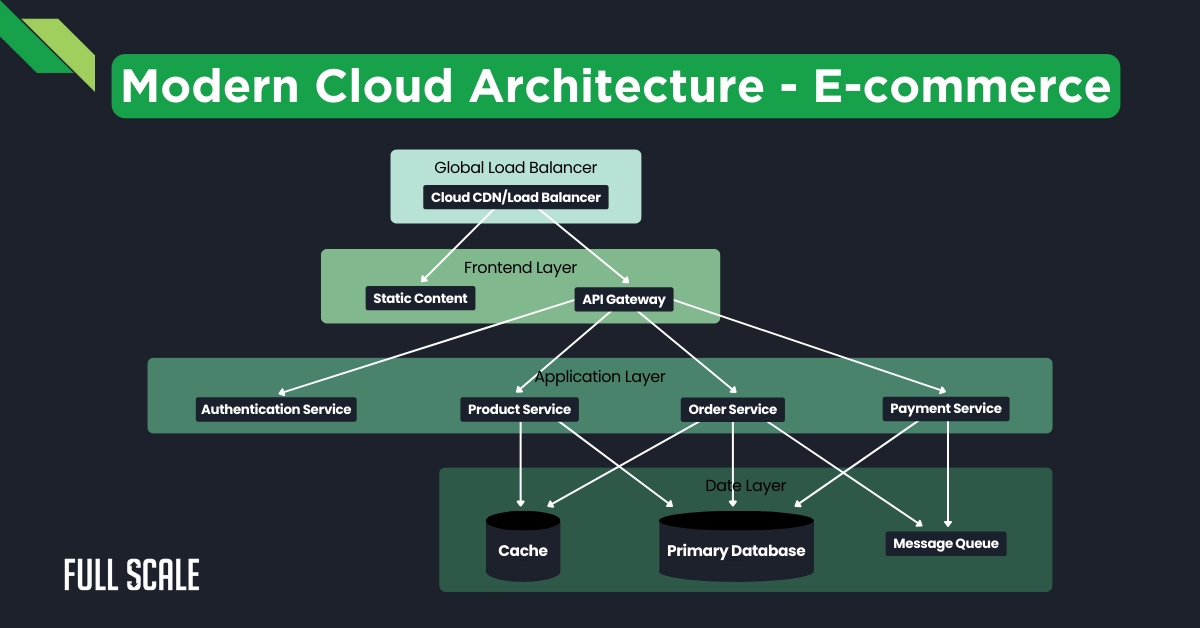
This e-commerce implementation demonstrates how platform engineering principles translate into tangible business outcomes. Building on these architectural insights, organizations must next consider the financial implications of their cloud infrastructure, which brings us to FinOps-driven architecture.
B. FinOps-Driven Architecture
Cloud architecture cost optimization has become a critical success factor. FinOps principles now directly influence architectural decisions and design patterns.
Cost-Aware Architectural Decisions
Organizations must integrate cost consciousness into their cloud-native architecture design:
| Strategy | Implementation | Cost Impact |
| Resource Right-sizing | AI-powered optimization | 30-45% savings |
| Auto-scaling Rules | Demand-based provisioning | 25-35% reduction |
| Multi-cloud Strategy | Workload distribution | 20-30% optimization |
| Storage Tiering | Automated data lifecycle | 40-50% storage savings |
Dynamic Resource Optimization
Modern cloud architecture requires intelligent resource management:
- Automated capacity planning
- Workload-aware scaling
- Spot instance utilization
- Reserved instance optimization
Enterprise Case Study: Resource Optimization A global retail platform achieved significant savings:
- Overall cloud costs reduced by 42%
- Computing efficiency improved by 35%
- Storage costs optimized by 48%
- Resource utilization increased by 60%
C. Serverless-First Design
Serverless architecture adoption continues to reshape cloud computing architecture. This approach prioritizes business logic over infrastructure management.
Beyond Function-as-a-Service
Modern serverless architectures encompass:
| Component | Use Case | Benefits |
| Event-driven Processing | Real-time data handling | 70% cost reduction |
| API Management | Scalable interfaces | 85% less maintenance |
| Database Services | Auto-scaling storage | 60% operational savings |
| Queue Processing | Asynchronous workflows | 50% improved efficiency |
Container-based Serverless
The convergence of containerization and serverless offers new possibilities:
- Kubernetes-native serverless platforms
- Custom runtime environments
- Enhanced local development
- Improved debugging capabilities
Implementation Success Metrics:
- Development velocity increased by 40%
- Operational overhead reduced by 65%
- Time-to-market accelerated by 50%
- Infrastructure costs optimized by 35%
Emerging Cloud Architecture Best Practices 2025 Patterns to Watch
Cloud architecture patterns continue to evolve as new technologies emerge. These patterns represent significant shifts in how organizations design and implement cloud solutions.
A. Edge-Native Architectures
Edge computing architecture represents a fundamental shift in cloud computing design. This pattern optimizes application performance by processing data closer to its source.
Edge Computing Integration
Modern cloud architecture best practices increasingly incorporate edge computing capabilities:
| Component | Purpose | Implementation Impact |
| Edge Nodes | Local processing | 65% latency reduction |
| Data Caching | Content delivery | 40% bandwidth savings |
| Local Analytics | Real-time insights | 80% faster processing |
| Security Controls | Distributed protection | 50% threat reduction |
Real-World Applications:
- IoT device management platforms
- Content delivery networks
- Gaming infrastructure
- Industrial automation systems
Data Locality Considerations
Cloud-native architecture must address data sovereignty requirements:
- Regional compliance frameworks
- Data residency requirements
- Privacy regulation adherence
- Cross-border data flows
Case Study: Global Manufacturing A manufacturing enterprise implemented edge computing:
- Processing latency reduced by 75%
- Network costs decreased by 45%
- Real-time analytics improved by 60%
- Compliance costs reduced by 30%
B. AI/ML-Optimized Infrastructure
Cloud architecture design now incorporates specialized patterns for AI and ML workloads. These patterns optimize resource utilization and model performance.
ML-Specific Architecture Patterns
| Pattern | Application | Benefits |
| GPU Clusters | Model training | 4x training speed |
| Inference Endpoints | Production deployment | 70% cost reduction |
| Feature Stores | Data management | 50% development efficiency |
| Model Registry | Version control | 40% governance improvement |
GPU/TPU Optimization Strategies
Modern cloud computing architecture requires specialized hardware optimization:
- Auto-scaling ML workloads
- Resource allocation algorithms
- Cost-aware training schedules
- Multi-tenant GPU sharing
ML Pipeline Architecture Case Study: An e-commerce platform optimized their ML infrastructure:
- Model training time reduced by 65%
- Infrastructure costs decreased by 45%
- Prediction latency improved by 55%
- Development cycle shortened by 40%
Implementation Challenges
Organizations face several challenges when adopting these patterns:
1. Technical Complexity
- Specialized skill requirements
- Integration difficulties
- Performance optimization needs
2. Operational Overhead
- Monitoring complexity
- Management tools
- Resource coordination
3. Cost Management
- Hardware investments
- Training requirements
- Operational expenses
Success Metrics
Organizations should track these key metrics:
| Metric Category | Key Indicators | Target Improvement |
| Performance | Response time, throughput | 40-60% improvement |
| Cost | Resource utilization, ROI | 30-50% reduction |
| Reliability | Uptime, error rates | 99.99% availability |
| Security | Threat detection, compliance | 70% risk reduction |
Overrated Trends to Approach Cautiously
Cloud architecture best practices require careful evaluation of trending patterns. Some popular approaches may not deliver the expected value without proper context and implementation strategy.
Multi-cloud for Multi-cloud’s Sake
Organizations often pursue multi-cloud architecture strategies without clear business justification. This approach can introduce unnecessary complexity and costs.
| Challenge | Impact | Risk Mitigation |
| Skill Requirements | 2-3x training costs | Focus on primary cloud expertise |
| Tool Complexity | 40% operational overhead | Standardize on cross-platform tools |
| Security Management | 65% increased attack surface | Implement unified security controls |
| Cost Management | 35% higher cloud spend | Optimize workload placement |
Blockchain in Enterprise Architecture
While blockchain offers specific use cases, its integration into cloud computing architecture requires careful consideration:
Common Pitfalls:
- Over-engineering simple workflows
- Unnecessary decentralization
- High operational costs
- Complex maintenance requirements
Over-Engineered Microservices
Microservices architecture trends must align with organizational capabilities:
| Anti-Pattern | Impact | Alternative Approach |
| Too Fine-Grained | 50% increased complexity | Domain-driven service boundaries |
| Premature Adoption | 40% development overhead | Gradual monolith decomposition |
| Poor Service Boundaries | 60% integration issues | Business capability alignment |
| Inconsistent Patterns | 45% maintenance burden | Standardized service templates |
Data Mesh Without Clear Use Cases
Modern cloud architecture design must validate data mesh requirements:
Implementation Risks:
- Organizational readiness gaps
- Technical complexity overhead
- Governance challenges
- Resource allocation issues
Implementation Strategy
Success in cloud-native architecture requires a systematic approach to adoption and implementation.
A. Assessment Framework
Organizations need structured evaluation methods for cloud architecture patterns:
| Assessment Area | Key Considerations | Success Metrics |
| Business Impact | ROI, Time-to-market | 30% efficiency gain |
| Technical Feasibility | Skill gaps, tools | 90% implementation success |
| Team Capability | Training needs, expertise | 60% productivity improvement |
| Risk Profile | Security, compliance | 80% risk mitigation |
Business Impact Evaluation
- Revenue potential analysis
- Cost reduction opportunities
- Market competitiveness impact
- Customer experience improvements
Technical Feasibility Analysis
- Infrastructure requirements
- Integration complexity
- Performance implications
- Scalability considerations
Team Capability Assessment
- Current skill inventory
- Training requirements
- Resource availability
- Knowledge transfer plans
B. Adoption Roadmap
Cloud architecture implementation requires careful planning and systematic execution. Organizations must balance rapid adoption with sustainable growth.
Phased Implementation Approach
Modern cloud architecture design demands a structured rollout strategy:
| Phase | Objectives | Duration | Key Deliverables |
| Phase 1: Assessment | Infrastructure audit, requirement gathering | 4-6 weeks | Gap analysis, architecture blueprint |
| Phase 2: Foundation | Core infrastructure setup, baseline security | 8-10 weeks | Base platform, security controls |
| Phase 3: Migration | Workload transition, integration testing | 12-16 weeks | Migrated applications, test results |
| Phase 4: Optimization | Performance tuning, cost optimization | Ongoing | Efficiency metrics, cost savings |
Critical Success Factors:
- Clear milestones and success criteria
- Continuous stakeholder communication
- Regular progress assessment
- Iterative feedback incorporation
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Cloud-native architecture implementation requires comprehensive risk management:
| Risk Category | Mitigation Approach | Monitoring Metrics |
| Technical | Architecture reviews, POC validation | System stability, error rates |
| Security | Zero-trust implementation, compliance checks | Threat detection, audit results |
| Operational | Automated failover, disaster recovery | Uptime, recovery time |
| Business | Cost controls, performance SLAs | Budget adherence, user satisfaction |
Implementation Safeguards:
- Automated rollback capabilities
- Blue-green deployment strategies
- Comprehensive monitoring systems
- Regular security assessments
Team Upskilling Requirements
Cloud computing architecture demands continuous learning and skill development:
| Skill Area | Training Focus | Expected Outcome |
| Cloud Platforms | Platform-specific certifications | Certified cloud architects |
| DevOps Practices | CI/CD, Infrastructure as Code | Automated deployment pipelines |
| Security | Cloud security protocols, compliance | Secure architecture implementation |
| Cost Management | FinOps principles, optimization | Efficient resource utilization |
Skill Development Plan:
- Technical certification roadmap
- Hands-on laboratories
- Mentorship programs
- Knowledge sharing sessions
Implementation Strategy
Success in cloud-native architecture requires a systematic approach to adoption and implementation.
A. Assessment Framework
Organizations need structured evaluation methods for cloud architecture patterns:
| Assessment Area | Key Considerations | Success Metrics |
| Business Impact | ROI, Time-to-market | 30% efficiency gain |
| Technical Feasibility | Skill gaps, tools | 90% implementation success |
| Team Capability | Training needs, expertise | 60% productivity improvement |
| Risk Profile | Security, compliance | 80% risk mitigation |
Business Impact Evaluation
- Revenue potential analysis
- Cost reduction opportunities
- Market competitiveness impact
- Customer experience improvements
Technical Feasibility Analysis
- Infrastructure requirements
- Integration complexity
- Performance implications
- Scalability considerations
Team Capability Assessment
- Current skill inventory
- Training requirements
- Resource availability
- Knowledge transfer plans
B. Adoption Roadmap
Cloud architecture implementation requires careful planning and systematic execution. Organizations must balance rapid adoption with sustainable growth.
Phased Implementation Approach
Modern cloud architecture design demands a structured rollout strategy:
| Phase | Objectives | Duration | Key Deliverables |
| Phase 1: Assessment | Infrastructure audit, requirement gathering | 4-6 weeks | Gap analysis, architecture blueprint |
| Phase 2: Foundation | Core infrastructure setup, baseline security | 8-10 weeks | Base platform, security controls |
| Phase 3: Migration | Workload transition, integration testing | 12-16 weeks | Migrated applications, test results |
| Phase 4: Optimization | Performance tuning, cost optimization | Ongoing | Efficiency metrics, cost savings |
Critical Success Factors:
- Clear milestones and success criteria
- Continuous stakeholder communication
- Regular progress assessment
- Iterative feedback incorporation
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Cloud-native architecture implementation requires comprehensive risk management:
| Risk Category | Mitigation Approach | Monitoring Metrics |
| Technical | Architecture reviews, POC validation | System stability, error rates |
| Security | Zero-trust implementation, compliance checks | Threat detection, audit results |
| Operational | Automated failover, disaster recovery | Uptime, recovery time |
| Business | Cost controls, performance SLAs | Budget adherence, user satisfaction |
Implementation Safeguards:
- Automated rollback capabilities
- Blue-green deployment strategies
- Comprehensive monitoring systems
- Regular security assessments
Measuring Success
Cloud architecture best practices require clear success metrics. Organizations must establish comprehensive measurement frameworks to validate their implementation effectiveness.
Key Performance Indicators
Modern cloud architecture design success relies on measurable outcomes:
| Metric Category | KPI | Target Range | Measurement Frequency |
| Performance | Response time | <100ms | Real-time |
| Throughput | >1000 req/sec | Hourly | |
| Error rate | <0.1% | Daily | |
| Architecture Efficiency | Resource utilization | 70-80% | Daily |
| Deployment frequency | >10/day | Weekly | |
| Mean time to recovery | <10 minutes | Monthly |
Architecture Efficiency Metrics
Cloud-native architecture requires specific efficiency measurements:
Technical Metrics
- System uptime: 99.99%
- API response times: <50ms
- Cache hit ratio: >90%
- Queue processing time: <1s
Development Metrics
- Code deployment frequency
- Change failure rate
- Mean time to deployment
- Technical debt ratio
Cost Optimization Benchmarks
Cloud architecture cost optimization tracking includes:
| Cost Category | Metric | Target Improvement |
| Infrastructure | Resource utilization | 30% reduction |
| Idle resource cost | 50% reduction | |
| Development | Deployment automation | 40% time savings |
| Testing automation | 60% cost reduction |
Developer Productivity Measures
Effective cloud computing architecture enhances team productivity:
| Productivity Metric | Baseline | Target | Impact |
| Deployment Time | 2 hours | 15 minutes | 87% improvement |
| Bug Resolution | 48 hours | 4 hours | 92% reduction |
| Feature Delivery | 2 weeks | 3 days | 70% faster |
| Code Review Time | 24 hours | 2 hours | 90% reduction |
Success Validation Framework
Organizations should implement structured validation processes:
Quantitative Metrics
1. System Performance
- Transaction throughput
- Resource efficiency
- Error rates
- Response times
2. Business Impact
- Cost savings
- Revenue impact
- Market response
- Customer satisfaction
Qualitative Assessments
1. Team Effectiveness
- Developer satisfaction
- Knowledge sharing
- Innovation metrics
- Collaboration quality
2. Operational Excellence
- Process improvements
- Security posture
- Compliance status
- Risk reduction
Continuous Improvement Indicators
Cloud architecture implementation requires ongoing optimization:
| Area | Metric | Review Frequency |
| Technical Debt | Code quality scores | Weekly |
| Security Posture | Vulnerability counts | Daily |
| Cost Efficiency | Resource optimization | Monthly |
| Team Performance | Velocity metrics | Bi-weekly |
Future Outlook for Cloud Architecture
Cloud architecture best practices continue to evolve rapidly. Understanding emerging patterns helps organizations prepare for future technological shifts.
Upcoming Architectural Patterns
Modern cloud architecture design is shifting toward new paradigms:
| Pattern | Timeline | Business Impact | Implementation Complexity |
| Quantum-Ready Infrastructure | 2025-2026 | High | Very High |
| AI-Driven Architecture | 2025 | High | Medium |
| Green Computing Design | 2025 | Medium | Low |
| Autonomous Systems | 2026 | High | High |
Key Emerging Technologies
1. Quantum Computing Integration
- Hybrid quantum-classical architectures
- Quantum-safe security protocols
- Specialized quantum algorithms
- Hardware abstraction layers
2. Advanced AI Operations
- Self-healing infrastructure
- Predictive scaling
- Automated optimization
- Intelligent security responses
Preparing for Future Changes
Cloud computing architecture requires forward-looking preparation:
| Area | Preparation Strategy | Expected Impact |
| Infrastructure | Modular design patterns | 60% future-proofing |
| Security | Zero-trust evolution | 80% risk reduction |
| Scalability | Edge-native readiness | 70% performance gain |
| Sustainability | Green computing practices | 40% efficiency improvement |
Long-term Sustainability Considerations
Cloud-native architecture must address environmental impact:
Environmental Metrics
- Carbon footprint tracking
- Energy efficiency ratings
- Resource optimization scores
- Sustainability compliance
Implementation Strategies
1. Green Computing Initiatives
- Energy-efficient algorithms
- Sustainable resource management
- Carbon-aware scheduling
- Renewable energy integration
2. Resource Optimization
- Workload consolidation
- Intelligent cooling systems
- Power usage effectiveness
- Hardware lifecycle management
Strategic Recommendations
Organizations should focus on these key areas:
| Priority | Action Item | Timeline |
| High | AI/ML Infrastructure | Q2 2025 |
| High | Edge Computing Framework | Q3 2025 |
| Medium | Quantum Readiness | Q4 2025 |
| Medium | Green Computing | Q1 2026 |
Technology Investment Areas
Future-proof cloud architecture requires strategic investment:
1. Core Technologies
- Containerization evolution
- Serverless advancement
- Edge computing maturity
- AI/ML infrastructure
2. Support Systems
- Advanced monitoring tools
- Security frameworks
- Automation platforms
- Sustainability measures
Risk Management Strategy
Future cloud computing architecture faces evolving challenges:
| Risk Category | Mitigation Approach | Review Frequency |
| Technical Obsolescence | Regular architecture reviews | Quarterly |
| Security Threats | Advanced threat modeling | Monthly |
| Compliance Changes | Regulatory monitoring | Bi-monthly |
| Resource Constraints | Capacity planning | Monthly |
Innovation Roadmap
Organizations should prepare for emerging trends:
1. Near-term (2025)
- AI-driven operations
- Edge computing expansion
- Green computing initiatives
- Advanced security measures
Stay Ahead with Cutting-Edge Cloud Architecture through Full Scale
Cloud architecture is evolving rapidly, and adopting the right trends is essential for staying competitive. Full Scale specializes in helping businesses implement scalable, secure, and cost-effective cloud solutions tailored to their unique needs.
Why Choose Full Scale?
- Expert Cloud Developers: Access top-tier talent skilled in the latest cloud technologies and frameworks.
- Scalable Solutions: Build a cloud architecture that grows with your business.
- End-to-End Support: From planning to implementation, we ensure a seamless transition to modern cloud strategies.
- Cost-Effective Excellence: Maximize your ROI with efficient and future-proof solutions.
Don’t get left behind. Partner with Full Scale to adopt the cloud architecture trends that will power your business into the future.
Talk to Our Cloud Experts
FAQs: Cloud Architecture
What is cloud-native architecture?
Cloud native architecture represents applications and services built specifically for cloud environments. This approach maximizes cloud computing capabilities through containerization, microservices, and automated scaling.
What is hybrid cloud architecture?
Hybrid cloud architecture combines private and public cloud infrastructure into a single, flexible computing environment. This model enables organizations to maintain sensitive workloads on-premise while leveraging public cloud scalability.
What is multi-cloud architecture?
Multi-cloud architecture involves using multiple cloud computing services from different providers. This approach helps organizations optimize costs, reduce vendor lock-in, and leverage best-of-breed services.
What is cloud computing architecture?
Cloud computing architecture encompasses the components and subcomponents required for successful cloud computing. This includes all front-end and back-end elements, plus the cloud-based delivery network.
What are the 4 types of cloud architecture?
The four types are:
- Public cloud: Shared infrastructure managed by providers
- Private cloud: Dedicated infrastructure for single organizations
- Hybrid cloud: Combination of public and private clouds
- Community cloud: Shared infrastructure for specific communities
What do you mean by cloud architecture?
Cloud architecture describes how technology components combine to build a cloud infrastructure. It includes storage, servers, database management, networking, and software capabilities delivered via the Internet.
What exactly does a cloud architect do?
A cloud architect designs and oversees cloud computing strategy. They manage cloud adoption plans, application design, and system architecture while ensuring proper implementation of cloud technologies.
What are the three layers of cloud architecture?
The three fundamental layers are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Computing resources and storage
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Development and deployment environment
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Application delivery and management



