A Practical CTO s Guide to Bug Prioritization Framework for Remote Teams
Bug prioritization presents unique challenges for distributed development teams working across multiple time zones.
Remote teams must balance urgent fixes with feature development while maintaining clear communication channels and consistent assessment criteria.
According to the 2023 State of DevOps Report, organizations lose an average of $2.5 million annually due to delayed bug fixes and insufficient defect management processes. The IBM Systems Sciences Institute reports that fixing bugs in production costs 4-5 times more than addressing them during development.
Traditional bug prioritization methods break down in remote settings due to:
- Asynchronous communication delays between team members
- Inconsistent severity assessments across different locations
- Timezone constraints affecting emergency response times
- Limited visibility into local context and user impact
- Challenges in reproducing environment-specific issues
The increasing complexity of modern software systems, combined with these distributed team challenges, demands a more structured approach to bug management and defect prioritization.
The True Cost of Poor Bug Prioritization
When remote teams lack an effective bug prioritization framework, the impact extends far beyond immediate technical issues. Understanding these costs helps organizations justify investing in robust defect management processes.
Impact on Development Velocity
Poor bug prioritization severely impacts sprint velocity and release schedules. According to industry research:
- Development teams spend 20-40% of their time handling unplanned bug fixes
- Critical feature releases face delays due to urgent bug resolution
- Context switching between bugs and features reduces productivity by 25%
Resource Allocation Inefficiencies
Mismanaged bug prioritization leads to significant resource waste:
- Senior developers spend excessive time on low-priority issues
- Junior developers struggle with complex bugs beyond their expertise
- QA teams face bottlenecks due to unclear testing priorities
- Product managers devote extra hours to bug-related communications
Technical Debt Accumulation
Ineffective bug management contributes to mounting technical debt:
- Minor bugs evolve into major system issues
- Temporary fixes become permanent solutions
- Documentation gaps widen as quick fixes accumulate
- System complexity increases with each workaround
Team Morale and Productivity Effects
Poor bug prioritization takes a toll on team dynamics:
- Developer frustration grows with unclear bug severity guidelines
- Team confidence decreases as issues remain unresolved
- Cross-team collaboration suffers from priority conflicts
- Sprint planning becomes unpredictable and reactive
Customer Satisfaction Metrics
The business impact of poor bug management is reflected in key metrics:
- Customer satisfaction scores drop by 15% when critical bugs persist
- User retention decreases due to recurring issues
- Support ticket volume increases by 30%
- Feature adoption rates decline due to quality concerns
Building Your Bug Prioritization Framework
An effective bug prioritization framework helps distributed teams systematically evaluate and address software defects. This structured approach ensures consistent assessment across different time zones and team locations.
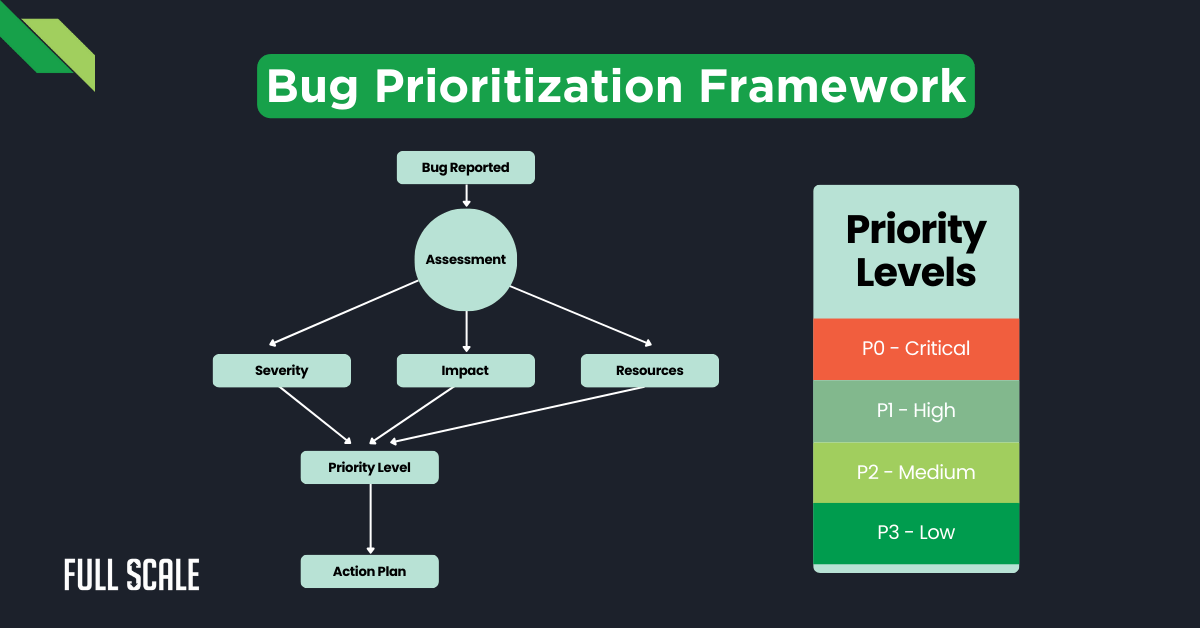
1. Severity Classification
The foundation of any bug prioritization framework begins with clear severity levels. This classification system helps remote teams maintain consistency in their defect assessment process.
The following table outlines a comprehensive severity classification system for distributed teams:
| Severity Level | Description | Examples | Response Time | Team Escalation |
| Critical (P0) | System-wide failures affecting core functionality | Payment system outage; Security breach; Data loss incidents | Immediate | Senior developers; DevOps team; Product owner |
| High (P1) | Major feature breakdowns with significant user impact | Authentication failures; API integration issues; Data consistency errors | Within 4 hours | Development lead; QA lead |
| Medium (P2) | Non-critical functionality issues | Performance degradation; UI/UX inconsistencies; Minor feature bugs | Within 24 hours | Development team; QA team |
| Low (P3) | Minor improvements and cosmetic issues | Visual glitches; Typography errors; Documentation updates | Next sprint | Regular sprint planning |
2. Assessment Criteria Matrix
The assessment criteria matrix provides distributed teams with a standardized approach to evaluate bug impact and priority. This framework considers multiple factors affecting both technical and business aspects.
Business Impact Evaluation
The following matrix helps teams assess the business implications of each bug:
| Impact Factor | High (5 points) | Medium (3 points) | Low (1 point) |
| Revenue Effect | Direct revenue loss; Payment failures; Customer churn | Indirect revenue impact; Feature limitations; User friction | No revenue impact; Cosmetic issues; Minor inconveniences |
| User Experience | Core functionality blocked; Data corruption risk; System unavailable | Workflow disruption; Performance issues; Feature limitations | Visual inconsistencies; Minor delays; Alternative available |
| Compliance Risk | Regulatory violations; Legal exposure; Data privacy breach | Policy deviations; Documentation gaps; Audit findings | No compliance impact; Internal standards; Best practices |
Technical Assessment Factors
Remote teams should evaluate these technical aspects for each bug:
| Factor | Critical Considerations | Implementation Impact |
| Scope of Impact | Number of affected systems; User base percentage; Geographic reach | Resource allocation; Timeline estimation; Team coordination |
| Implementation Complexity | Technical debt risk; System dependencies; Testing requirements | Development effort; QA coverage; Deployment complexity |
| Resource Requirements | Specialized expertise; Time zone coverage; Tool dependencies | Team availability; Knowledge transfer; Documentation needs |
Resource Considerations
Resource evaluation is critical for effective bug prioritization in distributed teams. This assessment ensures proper allocation of team capabilities across time zones.
| Resource Factor | Assessment Criteria | Implementation Considerations |
| Required Expertise | Senior developer availability; Domain knowledge; Technical specialization | Skills mapping; Knowledge sharing; Training needs |
| Time Zone Dependencies | Coverage hours; Handoff requirements; Emergency response | Team overlap periods; Communication protocols; Backup arrangements |
| Development Effort | Task complexity; Testing requirements; Integration needs | Story points estimation; Sprint capacity; Resource blocking |
This resource assessment framework helps remote teams:
- Match bug complexity with available expertise
- Ensure adequate coverage across time zones
- Accurately estimate development efforts
- Plan resource allocation efficiently
Remote-Specific Considerations
Distributed teams face unique challenges in bug prioritization that require specialized protocols and tools. This section outlines essential considerations for effective remote bug management.
1. Asynchronous Communication Protocols
Remote bug prioritization demands structured communication to overcome time zone barriers. Teams must establish clear protocols that facilitate effective information sharing and decision-making.
Structured Bug Reporting Template
A standardized bug reporting template ensures consistent information collection across distributed teams. Each field serves a specific purpose in facilitating accurate bug assessment and resolution.
| Field | Description | Required Information | Validation Criteria |
| Summary | Brief bug description | Clear, concise overview; Priority level; Component affected | Must follow naming convention; Include priority tag |
| Steps to Reproduce | Detailed reproduction steps | Numbered list; Environment details; Preconditions | Minimum 3 steps; Include all prerequisites |
| Expected Result | Intended behavior | Clear description; Business context; User impact | Reference to requirements; User story link |
| Actual Result | Current behavior | Bug manifestation; Error messages; Impact scope | Screenshots required; Error logs attached |
| Environment | System configuration | OS; Browser; Versions; Database state | Version numbers; Configuration details |
| Supporting Evidence | Visual documentation | Screenshots; Videos; Console logs | Maximum file size; Required format |
Time Zone Management Protocols
Time zone differences require clear protocols for bug handling across different shifts. These protocols ensure continuous coverage and timely response to critical issues.
| Scenario | Protocol | Response Time SLA |
| Critical Bug Detection | Emergency notification chain; Designated on-call responders | 15 minutes acknowledgment |
| Handoff Process | Documentation requirements; Status update format | End of each shift |
| Triage Meetings | Rotating schedule; Recording requirements | 24-hour completion cycle |
2. Collaboration Tools Stack
Remote teams require an integrated tool ecosystem for effective bug management. Each tool serves a specific purpose in the prioritization workflow.
Core Tool Requirements
The following table outlines essential tools needed for effective remote bug management. Each category addresses specific needs in the bug prioritization process.
| Tool Category | Primary Purpose | Essential Features | Integration Requirements |
| Issue Tracking | Bug workflow management | Custom fields; Automation rules; Priority matrices | API access; SSO support |
| Documentation | Knowledge sharing | Version control; Templates; Search functionality | Real-time collaboration |
| Communication | Team collaboration | Thread organization; Priority notifications | Mobile support; Alert systems |
| Video Documentation | Bug reproduction | Screen recording; Annotation tools | Cloud storage integration |
| Automated Testing | Regression detection | CI/CD integration; Report generation | Version control systems |
Tool Integration Framework
Successful bug management requires seamless integration between different tools. This framework ensures smooth data flow and consistent bug tracking across platforms.
| Integration Type | Purpose | Implementation Requirements |
| Primary Workflows | Automated bug creation; Status synchronization | API configuration; Webhook setup |
| Data Consistency | Unified priority schemes; Status mapping | Field mapping; Data validation |
| Notification Systems | Alert routing; Escalation paths | Rule configuration; User mapping |
Video Documentation Guidelines
Effective video documentation accelerates bug resolution in remote teams. These guidelines ensure clear and efficient video communication across time zones.
| Content Type | Required Elements | Maximum Duration |
| Bug Reproduction | Environment setup; Steps execution; Error demonstration | 3 minutes |
| Solution Verification | Fix implementation; Testing process; Success criteria | 5 minutes |
| Team Training | Process explanation; Tool usage; Best practices | 10 minutes |
Prioritization Implementation Guide
A structured implementation approach ensures the successful adoption of the bug prioritization framework across distributed teams. This section outlines essential steps and processes for effective deployment.
1. Setting Up the Process
Successful implementation begins with establishing core processes and tools. This phase focuses on creating the foundation for consistent bug prioritization through standardized training, tools, and documentation across all development teams.
Initial Team Training
Comprehensive training establishes a foundation for consistent framework application across all teams.
| Training Component | Duration | Key Deliverables | Success Criteria |
| Framework Overview | 2 days | Core concepts guide; Priority matrices | Assessment completion |
| Tool Training | 3 days | Hands-on exercises; System guides | Practical demonstration |
| Process Workshop | 2 days | Workflow documentation | Role-play scenarios |
| Assessment Practice | 3 days | Evaluation templates | Team certification |
Tool Configuration
Proper tool setup ensures seamless bug management workflow across distributed teams.
| Configuration Element | Setup Requirements | Validation Steps |
| Issue Tracking System | Priority schemes; Custom fields | Workflow testing |
| Communication Tools | Channel structure; Notifications | Alert verification |
| Documentation Platform | Template library; Access controls | Usage validation |
SLA Establishment
Service Level Agreements define response and resolution expectations for each bug priority level.
| Priority Level | Initial Response | Update Frequency | Resolution Target |
| P0 (Critical) | 15 minutes | Every 2 hours | 4 hours |
| P1 (High) | 1 hour | Every 4 hours | 24 hours |
| P2 (Medium) | 4 hours | Daily | 72 hours |
| P3 (Low) | 24 hours | Weekly | Next sprint |
Documentation Templates
Standardized templates ensure consistent information capture and effective communication.
| Template Type | Required Elements | Usage Guidelines | Review Process |
| Bug Report | Description; Steps; Impact | Include screenshots | Team lead review |
| Status Update | Progress; Blockers; Timeline | Daily updates | Stakeholder review |
| Resolution Record | Root cause; Solution; Testing | Code references | Peer validation |
2. Cross-Timezone Workflow
Effective bug management across different time zones requires coordinated processes and clear communication channels. This section outlines the essential workflows and protocols that ensure continuous bug tracking and resolution across global teams.
Bug Review Schedule
Regular review cycles maintain consistent bug assessment and prioritization across time zones.
| Time Zone | Review Time | Participants | Focus Areas |
| APAC (UTC+8) | 09:00 SGT | APAC team; EU handoff | New issues; Updates |
| EU (UTC+1) | 09:00 CET | EU team; US handoff | Ongoing bugs |
| US (UTC-8) | 09:00 PST | US team; APAC handoff | Critical reviews |
Emergency Protocols
Clear emergency procedures ensure rapid response to critical issues across all time zones.
| Scenario | First Response | Escalation Path | Resolution Time |
| Production Outage | On-call engineer | Team Lead → CTO | 4 hours max |
| Security Breach | Security team | CISO → CEO | 2 hours max |
| Data Issue | Database admin | Data Lead → CTO | 6 hours max |
Handoff Procedures
Structured handoffs maintain workflow continuity between teams across different time zones.
| Handoff Element | Required Information | Verification Steps | Documentation |
| Status Report | Active bugs; Updates | Checklist review | Handoff log |
| Resource Update | Team availability | Capacity check | Allocation sheet |
| Risk Assessment | Potential issues | Review meeting | Risk register |
Communication Guidelines
Clear communication protocols ensure effective information sharing and collaboration across teams.
| Communication Type | Channel | Response Time | Format Requirements |
| Regular Updates | Issue tracker | Within 4 hours | Standard template |
| Urgent Matters | Emergency channel | Within 15 minutes | Alert format |
| Team Discussions | Team chat | Within 2 hours | Threaded format |
| Status Reports | Email/Documentation | Daily | Report template |
Quantifying Your Framework’s Impact
A data-driven approach to measuring bug prioritization effectiveness ensures continuous improvement and team alignment. This section outlines essential metrics and processes for evaluating framework success.
Key Metrics to Track
Quantifiable metrics provide objective insights into the framework’s effectiveness. These indicators help teams identify areas for improvement and validate process changes.
| Metric Category | Key Performance Indicator | Target | Measurement Method |
| Resolution Speed | Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) | P0: <4 hours; P1: <24 hours | Issue tracking analytics |
| Response Time | First Response Time | P0: <15 min; P1: <1 hour | Support system metrics |
| Quality Control | Bug Escape Rate | <5% of shipped features | Production monitoring data |
| Triage Accuracy | Priority Change Rate | <10% of triaged bugs | Issue tracking history |
| Team Efficiency | Sprint Bug Resolution Rate | >90% of planned fixes | Sprint velocity reports |
Performance Benchmarks
Industry benchmarks provide context for evaluating team performance and setting realistic improvement targets.
| Performance Area | Industry Average | Target Performance | Current Performance |
| Critical Bug MTTR | 6 hours | 4 hours | Tracked monthly |
| SLA Compliance | 85% | 95% | Tracked weekly |
| Customer Impact | 85% satisfaction | 95% satisfaction | Measured per release |
| Resource Utilization | 70% efficiency | 85% efficiency | Monitored daily |
Team Feedback Loops
Regular feedback mechanisms ensure continuous process refinement and team engagement.
| Review Type | Frequency | Key Participants | Primary Objectives |
| Daily Triage | Daily | Dev team; QA lead | Prioritization alignment; Blocker identification |
| Sprint Review | Weekly | Team leads; Product owner | Progress assessment; Resource adjustment |
| Process Retro | Bi-weekly | All team members | Process improvement; Pain point resolution |
| Stakeholder Review | Monthly | Management; Team leads | Strategic alignment; Resource planning |
Continuous Improvement Process
Systematic improvement ensures the framework evolves with changing team needs and project requirements.
| Improvement Area | Evaluation Method | Review Cycle | Action Items |
| Process Efficiency | Metric trending analysis | Monthly | Workflow optimization; Tool updates |
| Team Performance | Skill gap assessment | Quarterly | Training programs; Resource allocation |
| Tool Effectiveness | Usage analytics review | Bi-monthly | Integration improvements; Automation opportunities |
| Documentation | Completeness audit | Quarterly | Template updates; Guide revisions |
Each component of this measurement framework contributes to:
- Objective performance assessment
- Clear improvement targets
- Actionable insights
- Team accountability
Teams should review these metrics during sprint retrospectives and adjust processes based on the data-driven insights provided.
Case Study: Global E-commerce Platform Bug Management Transformation
This case study examines how a distributed development team successfully implemented the bug prioritization framework to improve their incident response and product quality.
Initial State
Before implementing the structured bug prioritization framework, the team faced significant challenges:
| Challenge Area | Initial Metrics | Business Impact |
| Resolution Time | 72-hour average MTTR | Customer dissatisfaction; Revenue loss |
| Team Efficiency | 45% bug resolution rate | Sprint delays; Feature backlog |
| Communication | 4-hour response delays | Increased escalations; Team friction |
| Priority Management | 65% priority accuracy | Resource misallocation; Critical delays |
Implementation Steps
The team followed a systematic approach to framework adoption:
| Phase | Duration | Key Actions | Outcomes |
| Assessment | 2 weeks | Process audit; Tool evaluation; Team surveys | Gap analysis report; Implementation roadmap |
| Setup | 3 weeks | Tool configuration; Template creation; SLA definition | Standardized workflow; Clear guidelines |
| Training | 2 weeks | Team workshops; Role-specific training; Hands-on practice | Skilled team members; Process alignment |
| Rollout | 4 weeks | Phased implementation; Daily monitoring; Quick adjustments | Smooth transition; Early wins |
Before/After Metrics
Quantifiable improvements demonstrated the framework’s effectiveness:
| Performance Indicator | Before | After | Improvement |
| Critical Bug MTTR | 72 hours | 4 hours | 94% reduction |
| First Response Time | 4 hours | 15 minutes | 94% reduction |
| Priority Accuracy | 65% | 95% | 46% increase |
| Team Satisfaction | 45% | 92% | 104% increase |
Lessons Learned
Key insights from the implementation process:
| Area | Learning | Application |
| Process Definition | Clear SLAs drive accountability | Established strict response times per priority level |
| Tool Integration | Automation reduces manual effort | Implemented automatic bug routing and notifications |
| Team Communication | Structured handoffs improve efficiency | Created standardized handoff templates |
| Training Impact | Regular practice sessions boost confidence | Instituted monthly refresher training |
Adaptation Strategies
The team developed effective strategies to overcome common challenges:
| Challenge | Solution | Impact |
| Time Zone Gaps | Implemented follow-the-sun model | 24/7 bug management coverage |
| Priority Conflicts | Created clear escalation paths | 85% reduction in priority disputes |
| Resource Constraints | Established skill-based routing | 40% improvement in resource utilization |
| Process Adoption | Introduced gamification elements | 95% team engagement in new process |
Success Factors
Critical elements that contributed to successful implementation.
1. Leadership Support
- Executive sponsorship
- Resource allocation
- Clear mandate
2. Team Engagement
- Regular feedback sessions
- Process ownership
- Recognition program
3. Tool Optimization
- Integrated toolchain
- Automated workflows
- Real-time dashboards
4. Continuous Improvement
- Weekly metrics review
- Process iterations
- Team suggestions
This case study demonstrates how systematic implementation of a bug prioritization framework can transform distributed team performance and product quality.
Critical Challenges and Strategic Solutions
Distributed teams often encounter specific challenges when implementing bug prioritization frameworks. This section outlines common pitfalls and provides practical solutions for each scenario.
Over-prioritization Traps
When everything becomes “high priority,” the prioritization framework loses its effectiveness. Here’s how to avoid priority inflation:
| Pitfall | Impact | Solution | Preventive Actions |
| Priority Inflation | Reduced responsiveness; Resource drain | Strict criteria enforcement | Weekly priority reviews; Approval workflows |
| Urgency Bias | Technical debt buildup; Poor resource use | Priority scoring system | Stakeholder training; Decision documentation |
| Scope Expansion | Delayed fixes; Wasted resources | Scope boundaries | Change tracking; Regular scope reviews |
Communication Breakdowns
Poor communication can derail even the best prioritization framework:
| Issue | Impact | Solution | Tools/Methods |
| Unclear Bug Reports | Extended fix time | Standardized templates | Issue templates; Screenshot tools |
| Missing Context | Wrong priority assignment | Required impact documentation | Context forms; System diagrams |
| Delayed Updates | Stakeholder confusion | Automated notifications | Status dashboards; Alert systems |
| Time Zone Issues | Missed deadlines | Global time protocols | Time converters; Schedule tools |
Tool Misuse
Improper tool usage can create inefficiencies and confusion:
| Issue | Impact | Solution | Implementation |
| Inconsistent Tracking | Inaccurate metrics | Standardized workflows | Tool training; Regular audits |
| Feature Underuse | Manual overhead | Feature education | Capability mapping; Usage guides |
| Integration Gaps | Data silos | System integration | API setup; Data sync rules |
Resource Allocation Mistakes
Poor resource management can undermine bug prioritization efforts:
| Issue | Impact | Solution | Action Items |
| Skill Mismatches | Slow resolution | Skill mapping | Assignment rules; Performance tracking |
| Overallocation | Team burnout | Capacity planning | Work limits; Load balancing |
| Knowledge Silos | Single points of failure | Cross-training | Pair programming; Documentation |
Prevention Strategies
To avoid these common pitfalls, teams should implement these preventive measures:
1. Regular Framework Reviews
- Monthly metric analysis
- Process adjustment cycles
- Team feedback sessions
2. Proactive Training
- New team member onboarding
- Regular skill updates
- Tool proficiency checks
3. Communication Enhancement
- Standard communication protocols
- Regular sync meetings
- Clear escalation paths
4. Resource Optimization
- Capacity planning
- Skill development
- Tool optimization
By recognizing these common pitfalls and implementing appropriate solutions, teams can maintain an effective bug prioritization framework that supports their development goals.
Taking Your Bug Prioritization Framework Forward
The implementation of an effective bug prioritization framework is essential for distributed development teams seeking to improve their software quality and team efficiency. This guide has outlined key components for success.
Framework Summary
Critical elements for successful bug prioritization include:
| Component | Key Benefits | Implementation Focus |
| Clear Process | Consistent decision-making | Priority criteria; Workflow definition |
| Tool Integration | Efficient tracking | Automation; Cross-platform sync |
| Team Alignment | Improved collaboration | Training; Communication protocols |
| Measurement System | Data-driven improvements | Metrics tracking; Regular reviews |
Next Steps for Implementation
1. Initial Assessment
- Evaluate current processes
- Identify improvement areas
- Document team needs
2. Framework Customization
- Adapt priority levels
- Define team workflows
- Configure tool integrations
3. Team Training
- Schedule workshops
- Create documentation
- Establish feedback loops
4. Continuous Evolution
- Monitor key metrics
- Gather team feedback
- Refine processes
Organizations implementing this framework should focus on gradual adoption while maintaining clear communication and regular assessment of results. Success depends on consistent application and ongoing refinement based on team needs and project requirements.
Streamline Bug Prioritization with Full Scale
Managing bugs effectively is critical for remote teams to deliver high-quality software on time.
At Full Scale, we specialize in helping businesses like yours build and manage remote development teams equipped with the skills and tools to streamline bug prioritization and resolution.
Why Full Scale?
- Expert Development Teams: Our skilled developers understand the nuances of agile workflows and bug management.
- Seamless Integration: Our teams integrate effortlessly with your existing processes, ensuring smooth collaboration.
- Tailored Solutions: We align with your priorities to ensure critical issues are resolved first.
- Increased Efficiency: Focus on strategic goals while we help you minimize disruptions caused by bugs.
Don’t let bugs derail your progress. Schedule a free consultation today to learn how Full Scale can help your remote team stay focused and productive.
Start Your Framework with Full Scale
FAQs: Bug Prioritization Framework
How long does it typically take to implement a bug prioritization framework for a distributed team?
Implementation typically takes 6-8 weeks for a mid-sized team (15-30 developers). This includes 2 weeks for initial setup, 2 weeks for tool configuration, and 2-4 weeks for team training and process refinement. Teams can expect to see measurable improvements in bug resolution times within the first month.
What are the essential tools needed to start implementing this framework?
The minimum required tools include an issue-tracking system (like JIRA or Linear), a team communication platform (like Slack), and a documentation system (like Confluence). Additional tools for video documentation and automated testing can be integrated gradually based on team needs.
How can we ensure consistent bug prioritization across different time zones?
Consistency is achieved through standardized priority criteria, detailed templates, and regular sync meetings. Teams should establish clear handoff procedures, use a shared priority matrix, and maintain detailed documentation. Regular calibration sessions between team leads help maintain alignment.
What metrics should we track to measure the framework’s effectiveness?
Key metrics include Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) for each priority level, first response time, priority accuracy rate (percentage of bugs that don’t require reprioritization), and team satisfaction scores. Track these metrics weekly for the first three months, then monthly for ongoing optimization.
How do we handle emergency bugs that occur outside of regular team hours?
Establish an on-call rotation system with clear escalation paths. Define specific criteria for “emergency” bugs and create detailed response protocols. Implement an automated alert system and maintain an up-to-date contact list for critical issues. Documentation should include troubleshooting guides for common critical scenarios.



